External cortical landmarks for localization of the hippocampus: Application for temporal lobectomy and amygdalohippocampectomy
- PMID: 30210904
- PMCID: PMC6122279
- DOI: 10.4103/sni.sni_446_17
External cortical landmarks for localization of the hippocampus: Application for temporal lobectomy and amygdalohippocampectomy
Abstract
Background: Accessing the hippocampus for amygdalohippocampectomy and minimally invasive procedures, such as depth electrode placement, require an accurate knowledge regarding the location of the hippocampus.
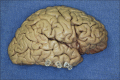
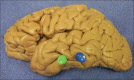
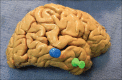
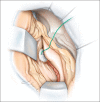
Methods: The authors removed 10 human cadaveric brains from the cranium and observed the relationships between the lateral temporal neocortex and the underlying hippocampus. They then measured the distance between the hippocampus and superficial landmarks. The authors also validated their study using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of 10 patients suffering from medial temporal lobe sclerosis where the distance from the hippocampal head to the anterior temporal tip was measured.
Results: In general, the length of the hippocampus was along the inferior temporal sulcus and inferior aspect of the middle temporal gyrus. Although the hippocampus tended to be more superiorly located in female specimens and on the left side, this did not reach statistical significance. The length of the hippocampus tended to be shorter in females, but this too failed to reach statistical significance. The mean distance from the anterior temporal tip to the hippocampal head was identical in the cadavers and MRIs of patients with medial temporal lobe sclerosis.
Conclusions: Additional landmarks for localizing the underlying hippocampus may be helpful in temporal lobe surgery. Based on this study, there are relatively constant anatomical landmarks between the hippocampus and overlying temporal cortex. Such landmarks may be used in localizing the hippocampus during amygdalohippocampectomy and depth electrode implantation in verifying the accuracy of image-guided methods and as adjuvant methodologies when these latter technologies are not used or are unavailable.
Keywords: Anatomy; epilepsy surgery; hippocampectomy; landmarks; neurosurgery; temporal lobe.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Superficial cortical landmarks for localization of the hippocampus: Application for temporal lobectomy and amygdalohippocampectomy.Surg Neurol Int. 2015 Feb 3;6:16. doi: 10.4103/2152-7806.150663. eCollection 2015. Surg Neurol Int. 2015. PMID: 25709853 Free PMC article.
-
External cortical landmarks and measurements for the temporal horn: Anatomic study with application to surgery of the temporal lobe.Surg Neurol Int. 2015 Feb 3;6:17. doi: 10.4103/2152-7806.150669. eCollection 2015. Surg Neurol Int. 2015. PMID: 25709854 Free PMC article.
-
Mesial temporal lobe morphology in intractable pediatric epilepsy: so-called hippocampal malrotation, associated findings, and relevance to presurgical assessment.J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2016 Jun;17(6):683-93. doi: 10.3171/2015.11.PEDS15485. Epub 2016 Feb 12. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 26870898
-
Selective amygdalohippocampectomy: the trans-middle temporal gyrus approach.Neurosurg Focus. 2008 Sep;25(3):E4. doi: 10.3171/FOC/2008/25/9/E4. Neurosurg Focus. 2008. PMID: 18759628 Review.
-
Modified Anterior Temporal Lobectomy: Anatomical Landmarks and Operative Technique.J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2015 Sep;76(5):407-14. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1549303. Epub 2015 May 22. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2015. PMID: 26008956 Review.
References
-
- Ayberk G, Yagli OE, Comert A, Esmer AF, Canturk N, Tekdemir I, et al. Anatomic relationship between the anterior sylvian point and the pars triangularis. Clin Anat. 2012;25:429–36. - PubMed
-
- Bronen RA, Cheung G. Relationship of hippocampus and amygdala to coronal MRI landmarks. Magn Reson Imaging. 1991;9:449–57. - PubMed
-
- Davies KG, Phillips BLB, Hermann BP. MRI confirmation of accuracy of freehand placement of mesial temporal lobe depth electrodes in the investigation of intractable epilepsy. Br J Neurosurg. 1996;10:175–8. - PubMed
-
- Duvernoy HM, Cattin F, Naidich TP, Fatterpekar G, Raybaud C, Risold PY, et al. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag; 2005. The Human Hippocampus.
-
- Naidich TP, Daniels DL, Haughton VM, Williams A, Pojunas K, Palacios E. Hippocampal formation and related structures of the limbic lobe: Anatomic-MR correlation. Part 1. Surface features and coronal sections. Radiology. 1987;162:747–54. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
