A three miRNAs signature for predicting the transformation of oral leukoplakia to oral squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 30210912
- PMCID: PMC6129488
A three miRNAs signature for predicting the transformation of oral leukoplakia to oral squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
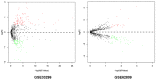
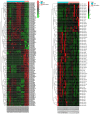
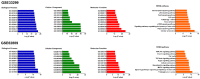
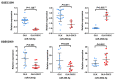
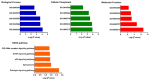
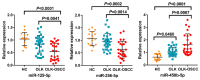
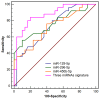
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) remains to be a global health problem. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms regulating the oral leukoplakia (OLK) to OSCC remain poorly known. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) expression profiles of GSE33299 and GSE62809 were downloaded from gene expression omnibus (GEO) respectively. R software and bioconductor packages were used to compare and identify the differentially expressed miRNAs between OLK tissues and OLK transformed OSCC (OLK-OSCC). The target genes of commonly changed miRNAs were then subjected to gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis, pathway analysis and miRNA-target genes network analysis. The prediction power of commonly changed miRNAs was further tested in an independent cohort. In total, 161 (88 upregulated and 73 downregulated) and 68 (19 upregulated and 49 downregulated) markedly altered miRNAs were identified from GSE33299 and GSE62809 respectively. The downstream targets of these differentially expression miRNAs in the two cohorts shared many top enriched GO and KEGG pathways. A set of three miRNAs signature including miR-129-5p, miR-296-5p and miR-450b-5p was commonly changed in both GSE33299 and GSE62809. Functional analysis revealed that the downstream target genes of the miRNA signature were associates with transcriptional regulation, estrogen signaling pathway, p53 signaling pathway and RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway. This three-gene signature was further successfully validated in another independent cohort. The expression levels of miR-129-5p and miR-296-5p were significantly downregulated in OLK-OSCC tissues compared to OLK tissues, while miR-450b-5p levels were higher in OLK-OSCC tissues. In addition, this three miRNAs signature could discriminate OLK from OLK-OSCC with high accuracy. In conclusion, our study has identified a three miRNAs signature that might help predict the transformation of OLK to OSCC. Which will provide useful guidance for therapeutic applications.
Keywords: Functional analysis; MicroRNAs; oral leukoplakia; oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Fuller CD, Wang SJ, Thomas CR Jr, Hoffman HT, Weber RS, Rosenthal DI. Conditional survival in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: results from the SEER dataset 1973-1998. Cancer. 2007;109:1331–43. - PubMed
-
- Rai V, Mukherjee R, Ghosh AK, Routray A, Chakraborty C. “Omics” in oral cancer: new approaches for biomarker discovery. Arch Oral Biol. 2018;87:15–34. - PubMed
-
- Wu L, Feng J, Shi L, Shen X, Liu W, Zhou Z. Candidal infection in oral leukoplakia: a clinicopathologic study of 396 patients from eastern China. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2013;17:37–40. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
