Effects of Nigella sativa Extracts on the Lipid Profile and Uncoupling Protein-1 Gene Expression in Brown Adipose Tissue of Mice
- PMID: 30211134
- PMCID: PMC6124217
- DOI: 10.4103/abr.abr_91_18
Effects of Nigella sativa Extracts on the Lipid Profile and Uncoupling Protein-1 Gene Expression in Brown Adipose Tissue of Mice
Abstract
Background: Uncoupling protein-1 (UCP-1) is the index protein of the brown adipose tissue (BAT), used in the obesity studies. We evaluated the effects of thymoquinone (TQ), hydroalcoholic, and hexane extracts of Nigella sativa, on the UCP-1 gene expression in BAT, and also on the recovery from oxidative stress, due to a high-fat diet.
Materials and methods: Fifty mice were divided into five groups: the first group was fed with a usual diet and the second, third, fourth, and fifth groups with a high-fat diet, hydroalcoholic extract, hexane extract, and TQ, respectively. After completing the course, the lipid profile, paraoxonase 1 (PON1), serum total antioxidant capacity (TAC), and malondialdehyde (MDA) were measured. UCP-1 expression in BAT was evaluated at the gene and protein level.
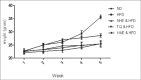
Results: The weight of mice, receiving TQ, hydroalcoholic, and hexane extracts, was decreased (P < 0.05), compared to the second group (P < 0.05). MDA was increased in the second group, compared to the first group (P < 0.05); however, TAC, liver catalase enzyme, and PON1 were decreased (P < 0.05). Furthermore, MDA of the third, fourth, and fifth groups had decreased, and the activity of PON1, liver catalase enzyme, and the amount of TAC was increased (P < 0.05). UCP-1 expression of the third and fourth groups was increased, compared to the second group (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: The results suggest that TQ, hydroalcoholic, and hexane extracts of N. sativa have a protective and therapeutic role in the oxidative stress, caused by high-fat diets. The hydroalcoholic and hexane extracts can induce weight loss, by positively affecting UCP-1, at the gene and protein level.
Keywords: Antioxidant capacity; Nigella sativa; malondialdehyde; obesity; uncoupling protein-1.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of Pioglitazone On the Lipid Profile, Serum Antioxidant Capacity, and UCP1 Gene Expression in Mouse Brown Adipose Tissue.Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2019 Apr;8(1):15-20. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31334282 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of hydroalcoholic extract of Nigella sativa seed on oxidative stress in hippocampus of STZ-induced diabetic rats.Avicenna J Phytomed. 2015 Jul-Aug;5(4):333-40. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2015. PMID: 26445713 Free PMC article.
-
Nigella sativa oil and thymoquinone reduce oxidative stress in the brain tissue of rats exposed to total head irradiation.Int J Radiat Biol. 2020 Feb;96(2):228-235. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2020.1683636. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Int J Radiat Biol. 2020. PMID: 31638880
-
Programming mediated by fatty acids affects uncoupling protein 1 (UCP-1) in brown adipose tissue.Br J Nutr. 2018 Sep;120(6):619-627. doi: 10.1017/S0007114518001629. Br J Nutr. 2018. PMID: 30176958 Review.
-
A Review on Possible Therapeutic Effect of Nigella sativa and Thymoquinone in Neurodegenerative Diseases.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2018;17(6):412-420. doi: 10.2174/1871527317666180702101455. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2018. PMID: 29962349 Review.
Cited by
-
A Review of the Potential Health Benefits of Nigella sativa on Obesity and Its Associated Complications.Plants (Basel). 2023 Sep 8;12(18):3210. doi: 10.3390/plants12183210. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37765374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemopreventive Efficacy of Thymoquinone in Chemically Induced Urinary Bladder Carcinogenesis in Rat.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Sep 15;2022:6276768. doi: 10.1155/2022/6276768. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36158887 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Properties, Phenolic Profile, and Botanical Aspect of Nigella sativa L. and Nigella damascena L. Seeds: A Comparative Study.Molecules. 2023 Jan 6;28(2):571. doi: 10.3390/molecules28020571. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36677629 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Nigella sativa Oil in Human Pre-Adipocytes.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Feb 25;8(2):51. doi: 10.3390/antiox8020051. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30823525 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Nigella sativa, Camellia sinensis, and Allium sativum as Food Additives on Metabolic Disorders, a Literature Review.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 17;12:762182. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.762182. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34867384 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

