Diagnostic Efficacy of Serum 1,3-β-D-glucan for Invasive Fungal Infection: An Update Meta-Analysis Based on 37 Case Or Cohort Studies
- PMID: 30211316
- PMCID: PMC6132083
- DOI: 10.1515/med-2018-0050
Diagnostic Efficacy of Serum 1,3-β-D-glucan for Invasive Fungal Infection: An Update Meta-Analysis Based on 37 Case Or Cohort Studies
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate the diagnostic performance of serum 1,3-β-D-gluan as biomarker for invasive fungal infection through meta-analysis.
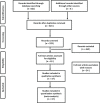
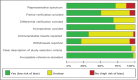
Methods: The electronic databases of Medline, Cochrane, Embase, Web of Science, OVID and CNKI were systematic searched to identified the case-control or Cohort studies relevant to diagnostic efficacy of serum 1,3-β-D-glucan for invasive fungal infection. The data of true positive (tp), false positive (fp), false negative (fn) and true negative (tn) patients number were extracted from each of the original included studies. The diagnostic sensitivity, specificity and systematic receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve were calculated and pooled through random or fixed effect method. The publication bias was evaluated by the Deek's funnel plot.
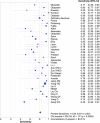
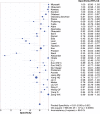
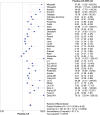
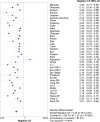
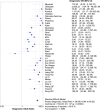
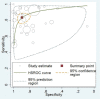
Results: Thirty-seven relevant studies were fulfilled the inclusion criteria and included in our present meta-analysis. The combined sensitivity, specificity, positive likely hood ratio (+lr), negative likely hood ratio (-lr) and diagnostic odds ratio(dor) for 1,3-β-D-glucan in diagnosis of invasive fungal infectionwere 0.83 (95%CI:0.38-0.61), 0.81 (95%CI:0.80-0.82), 5.13 (95%CI:3.98-6.62), 0.23 (95%CI:0.18-0.30), and 29.68 (95%CI:18.94-46.52) respectively. The pooled area under the ROC curve (AUC) was 0.91.The Deek's funnel plot asymmetry test showed there was no publication bias for 1,3-β-D-glucan in diagnosis of invasive fungal infection of the included 37 studies.
Conclusion: Serum 1,3-β-D-glucan assay was a promising biomarker for invasive fungal infection diagnosis.
Keywords: 1,3-β-D-glucan; diagnosis; invasive fungal infection; meta-analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Martino R, Lopez R, Sureda A, Brunet S, Domingo-Albós A.. Risk of reactivation of a recent invasive fungal infection in patients with hematological malignancies undergoing further intensive chemo-radiotherapy. A single-center experience and review of the literature. Haematologica. 1997;82:297–304. - PubMed
-
- García-Ruiz JC, Amutio E, Pontón J.. Invasive fungal infection in immunocompromised patients. Rev Iberoam Micol. 2004;21:55–62. - PubMed
-
- Ibáñez-Martínez E, Ruiz-Gaitán A, Pemán-García J.. Update on the diagnosis of invasive fungal infection. Rev Esp Quimioter. 2017;30(1):16–21. - PubMed
-
- Onishi A, Sugiyama D, Kogata Y, Saegusa J, Sugimoto T, Kawano S, Morinobu A, Nishimura K, Kumagai S.. Diagnostic accuracy of serum 1, 3-β-D-glucan for pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, invasive candidiasis, and invasive aspergillosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 2012;50:7–15. - PMC - PubMed
-
- He S, Hang JP, Zhang L, Wang F, Zhang DC, Gong FH.. A systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy of serum 1, 3-β-D-glucan for invasive fungal infection: Focus on cutoff levels. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2015;48:351–361. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
