Therapeutic opportunities for pain medicines via targeting of specific translation signaling mechanisms
- PMID: 30211342
- PMCID: PMC6130820
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ynpai.2018.02.001
Therapeutic opportunities for pain medicines via targeting of specific translation signaling mechanisms
Abstract
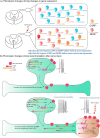
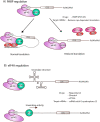
As the population of the world ages and as more and more people survive diseases that used to be primary causes of mortality, the incidence of severe chronic pain in most of the world has risen dramatically. This type of pain is very difficult to treat and the opioid overdose epidemic that has become a leading cause of death in the United States and other parts of the world highlights the urgent need to develop new pain therapeutics. A common underlying cause of severe chronic pain is a phenotypic change in pain-sensing neurons in the peripheral nervous system called nociceptors. These neurons play a vital role in detecting potentially injurious stimuli, but when these neurons start to detect very low levels of inflammatory meditators or become spontaneously active, they send spurious pain signals to the brain that are significant drivers of chronic pain. An important question is what drives this phenotypic shift in nociceptors from quiescence under most conditions to sensitization to a broad variety of stimuli and spontaneous activity. The goal of this review is to discuss the critical role that specific translation regulation signaling pathways play in controlling gene expression changes that drive nociceptor sensitization and may underlie the development of spontaneous activity. The focus will be on advances in technologies that allow for identification of such targets and on developments in pharmacology around translation regulation signaling that may yield new pain therapeutics. A key advantage of pharmacological manipulation of these signaling events is that they may reverse phenotypic shifts in nociceptors that drive chronic pain thereby creating the first generation of disease modifying drugs for chronic pain.
Keywords: AMPK; MNK; Nociceptor; Sensitization; eIF4A; eIF4E; mTOR.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Akopian A.N., Souslova V., England S., Okuse K., Ogata N., Ure J., Smith A., Kerr B.J., McMahon S.B., Boyce S., Hill R., Stanfa L.C., Dickenson A.H., Wood J.N. The tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channel SNS has a specialized function in pain pathways. Nat. Neurosci. 1999;2:541–548. - PubMed
-
- Atkins C.M., Davare M.A., Oh M.C., Derkach V., Soderling T.R. Bidirectional regulation of cytoplasmic polyadenylation element-binding protein phosphorylation by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II and protein phosphatase 1 during hippocampal long-term potentiation. J. Neurosci. 2005;25:5604–5610. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bai X., Ma D., Liu A., Shen X., Wang Q.J., Liu Y., Jiang Y. Rheb activates mTOR by antagonizing its endogenous inhibitor, FKBP38. Science. 2007;318:977–980. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

