Measurement of Intraoperative Blood Loss in Pediatric Orthopaedic Patients: Evaluation of a New Method
- PMID: 30211390
- PMCID: PMC6132334
- DOI: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-18-00014
Measurement of Intraoperative Blood Loss in Pediatric Orthopaedic Patients: Evaluation of a New Method
Abstract
Introduction: Our goal was to validate a new method of intraoperative blood loss measurement in pediatric patients who undergo orthopaedic surgery.
Methods: We prospectively collected surgical sponges from 55 patients who underwent pediatric posterior spinal fusion, single-event multilevel surgery, or hip reconstruction for measurement of intraoperative blood loss. We enrolled patients if expected estimated blood loss (EBL) was >200 mL. The methods used for blood loss assessment included the Triton sponge scanning system, visual method, gravimetric method, and measured assay (reference) method.
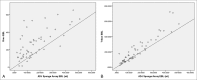
Results: The Triton system calculation of cumulative EBL per patient against the reference method yielded a strong positive linear correlation (R2 = 0.88). A weaker correlation was noted between the gravimetric method and reference EBL (R2 = 0.49). The Triton system had a low bias and narrow limits of agreement relative to the reference method (49 mL; 95% CI, 30 to 68). The gravimetric method had a higher bias and wider limits of agreement (101 mL; 95% CI, 67 to 135). The comparison of visual total EBL against the reference method yielded a notable discrepancy.
Discussion: Estimated blood loss measured using the Triton system correlated better with the reference method than with the gravimetric method. The visual estimation method was found to be inaccurate. Intraoperative use of the Triton system is convenient and precise for monitoring intraoperative blood loss.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Nowicki or an immediate family member serves as a paid consultant to Orthopediatrics and serves as a board member, owner, officer, or committee member of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons and the Pediatric Orthopaedic Society of North America. Mr. Satish or an immediate family member is an employee of and has stock or stock options held in Gauss Surgical. None of the following authors or any immediate family member has received anything of value from or has stock or stock options held in a commercial company or institution related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article: Dr. Ndika, Dr. Kemppainen, Dr. Cassidy, Dr. Forness, and Dr. Hassan. Dr. Nowicki performed data collection and manuscript preparation. Dr. Ndika, Dr. Kemppainen, Dr. Cassidy, and Dr. Forness performed data collection. Mr. Satish performed data analysis and manuscript preparation. Dr. Hassan performed data collection, data analysis, and manuscript preparation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Real-time evaluation of an image analysis system for monitoring surgical hemoglobin loss.J Clin Monit Comput. 2018 Apr;32(2):303-310. doi: 10.1007/s10877-017-0016-0. Epub 2017 Apr 7. J Clin Monit Comput. 2018. PMID: 28389913 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical evaluation of a novel system for monitoring surgical hemoglobin loss.Anesth Analg. 2014 Sep;119(3):588-594. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000000181. Anesth Analg. 2014. PMID: 24797122 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro evaluation of a novel system for monitoring surgical hemoglobin loss.Anesth Analg. 2014 Sep;119(3):595-600. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000000198. Anesth Analg. 2014. PMID: 24806138 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of common perioperative blood loss estimation techniques: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Clin Monit Comput. 2021 Apr;35(2):245-258. doi: 10.1007/s10877-020-00579-8. Epub 2020 Aug 19. J Clin Monit Comput. 2021. PMID: 32815042 Free PMC article.
-
Methods of Blood Loss Quantification in Major Abdominal Surgery: A Narrative Review.Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 2023;66(4):133-137. doi: 10.14712/18059694.2024.7. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 2023. PMID: 38588390 Review.
Cited by
-
Blood loss quantification during major abdominal surgery: prospective observational cohort study.BMC Surg. 2024 Jan 2;24(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12893-023-02288-w. BMC Surg. 2024. PMID: 38166991 Free PMC article.
-
Estimation of Blood Loss in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery by Measurements of Low Haemoglobin Levels in Mixtures of Blood, Saliva and Saline: a Laboratory Study.J Oral Maxillofac Res. 2021 Jun 30;12(2):e3. doi: 10.5037/jomr.2021.12203. eCollection 2021 Apr-Jun. J Oral Maxillofac Res. 2021. PMID: 34377380 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating surgical blood loss: A review of current strategies in various clinical settings.SAGE Open Med. 2024 Dec 16;12:20503121241308302. doi: 10.1177/20503121241308302. eCollection 2024. SAGE Open Med. 2024. PMID: 39691865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Triton sponge and canister app for estimating surgical blood loss.Saudi J Anaesth. 2019 Oct-Dec;13(4):390-391. doi: 10.4103/sja.SJA_38_19. Saudi J Anaesth. 2019. PMID: 31572095 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A better method for the dynamic, precise estimating of blood/haemoglobin loss based on deep learning of artificial intelligence.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Oct;8(19):1219. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-1806. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 33178751 Free PMC article.
References
-
-
Levels of evidence are described in the table of contents. In this article, references 11, 12, and 13 are level I studies. References 2, 5, 8, 9, 10, 18, and 19 are level II studies. References 1, 3, 4, 6, 15, 20, 21, 22, 24, and 25 are level III studies. References 16, 23, 26, and 27 are level IV studies. References 7, 14, and 17 are level V studies.
-
-
- Mooney JF, III, Barfield WR: Validity of estimates of intraoperative blood loss in pediatric spinal deformity surgery. Spine Deformity 2013;1:21-24. - PubMed
-
- Dildy GA, III, Paine AR, George NC, Velasco C: Estimating blood loss: Can teaching significantly improve visual estimation. Obstet Gynecol 2004;104:601-606. - PubMed
-
- Keenan WN, Griffiths H, Clegg J: Evaluating blood loss in children's orthopaedic surgery: A simplified method of photometric analysis of eluted swabs. J Pediatr Orthop 1998;18:488-491. - PubMed
-
- Chua S, Ho LM, Vanaja K, Nordstrom L, Roy AC, Arulkumaran S: Validation of a laboratory method of measuring postpartum blood loss. Gynecol Obstet Invest 1998;36:31-33. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

