Human eIF5 and eIF1A Compete for Binding to eIF5B
- PMID: 30211544
- PMCID: PMC6177315
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00839
Human eIF5 and eIF1A Compete for Binding to eIF5B
Abstract
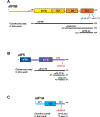
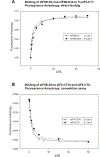
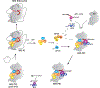
Eukaryotic translation initiation is a multistep process requiring a number of eukaryotic translation initiation factors (eIFs). Two GTPases play key roles in the process. eIF2 brings the initiator Met-tRNAi to the preinitiation complex (PIC). Upon start codon selection and GTP hydrolysis promoted by the GTPase-activating protein (GAP) eIF5, eIF2-GDP is displaced from Met-tRNAi by eIF5B-GTP and is released in complex with eIF5. eIF5B promotes ribosomal subunit joining, with the help of eIF1A. Upon subunit joining, eIF5B hydrolyzes GTP and is released together with eIF1A. We found that human eIF5 interacts with eIF5B and may help recruit eIF5B to the PIC. An eIF5B-binding motif was identified at the C-terminus of eIF5, similar to that found in eIF1A. Indeed, eIF5 competes with eIF1A for binding and has an ∼100-fold higher affinity for eIF5B. Because eIF5 is the GAP of eIF2, the newly discovered interaction offers a possible mechanism for coordination between the two steps in translation initiation controlled by GTPases: start codon selection and ribosomal subunit joining. Our results indicate that in humans, eIF5B displacing eIF2 from Met-tRNAi upon subunit joining may be coupled to eIF1A displacing eIF5 from eIF5B, allowing the eIF5:eIF2-GDP complex to leave the ribosome.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interaction between eukaryotic initiation factors 1A and 5B is required for efficient ribosomal subunit joining.J Biol Chem. 2006 Mar 31;281(13):8469-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600210200. Epub 2006 Feb 3. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16461768
-
eIF5 and eIF5B together stimulate 48S initiation complex formation during ribosomal scanning.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Oct 29;42(19):12052-69. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku877. Epub 2014 Sep 26. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25260592 Free PMC article.
-
Coupled release of eukaryotic translation initiation factors 5B and 1A from 80S ribosomes following subunit joining.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Mar;27(6):2384-97. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02254-06. Epub 2007 Jan 22. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17242201 Free PMC article.
-
The scanning mechanism of eukaryotic translation initiation.Annu Rev Biochem. 2014;83:779-812. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060713-035802. Epub 2014 Jan 29. Annu Rev Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24499181 Review.
-
Functional significance and mechanism of eIF5-promoted GTP hydrolysis in eukaryotic translation initiation.Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2001;70:207-31. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(01)70018-9. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11642363 Review.
Cited by
-
Established and Emerging Regulatory Roles of Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 5B (eIF5B).Front Genet. 2021 Aug 27;12:737433. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.737433. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34512736 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-range interdomain communications in eIF5B regulate GTP hydrolysis and translation initiation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jan 21;117(3):1429-1437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1916436117. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 31900355 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational rearrangements upon start codon recognition in human 48S translation initiation complex.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 May 20;50(9):5282-5298. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac283. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35489072 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the interaction dynamics of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2.Biochem Soc Trans. 2025 Jun 30;53(3):593-602. doi: 10.1042/BST20253022. Biochem Soc Trans. 2025. PMID: 40411218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The progress of protein synthesis factors eIFs, eEFs and eRFs in inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer pathogenesis.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 31;12:898966. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.898966. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36387239 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nanda JS, Saini AK, Munoz AM, Hinnebusch AG, and Lorsch JR (2013) Coordinated movements of eukaryotic translation initiation factors eIF1, eIF1A, and eIF5 trigger phosphate release from eIF2 in response to start codon recognition by the ribosomal preinitiation complex, J Biol Chem 288, 5316–5329. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zheng A, Yu J, Yamamoto R, Ose T, Tanaka I, and Yao M (2014) X-ray structures of eIF5B and the eIF5B-eIF1A complex: the conformational flexibility of eIF5B is restricted on the ribosome by interaction with eIF1A, Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 70, 3090–3098. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

