Correlation between esophageal pH-metry and esophagitis in gastroesophageal reflux disease in children
- PMID: 30212934
- PMCID: PMC6156075
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012042
Correlation between esophageal pH-metry and esophagitis in gastroesophageal reflux disease in children
Abstract
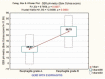
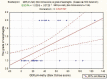
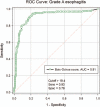
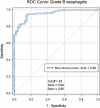
Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) is the intermittent or permanent passage of stomach content into the esophagus and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is the reflux which triggers a whole set of symptoms or complications. The study compares the 24-hours esophageal pH-metry, used for diagnosis of the GERD, with the esophagitis degree observed at the upper digestive endoscopy.72 children were included, aged over 4 years old, admitted in a pediatric gastroenterology regional center in Northeast Romania, diagnosed with GERD by 24 hours pH-metry (with a positive Boix-Ochoa score), which also underwent the upper digestive endoscopy.Out of the 72 children diagnosed with GERD, 47 (65.28%) had grade A esophagitis and 25 (34.72%) grade B esophagitis. In GERD associated with grade B esophagitis the Boix-Ochoa score is statistically significant higher, compared with the GERD associated with grade A esophagitis (F = 9.76, P = .0036, 95% CI).Upper digestive endoscopy performed in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease shows the constant presence of esophagitis at all patients. There were only grade A and B esophagitis due to the fact that they are young patients with a relative short history of the disease. The correlation tests show a perfect parallel between the pH-metry scores and the endoscopic lesion. The correlation is so accurate that the pH-metry scores can be sufficient to prove GERD and the grade of esophagitis, the upper digestive endoscopy being reserved only for the cases that does not respond to the medical treatment or have other complications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Correlation between the different pH-metry scores in gastroesophageal reflux disease in children.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Jun;95(26):e3804. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003804. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27367982 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori infection and gastroesophageal reflux in children.Dis Esophagus. 2016 Nov;29(8):1007-1012. doi: 10.1111/dote.12429. Epub 2015 Oct 12. Dis Esophagus. 2016. PMID: 26455913
-
Gastroesophageal reflux disease in infants: how much is predictable with questionnaires, pH-metry, endoscopy and histology?J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005 Feb;40(2):210-5. doi: 10.1097/00005176-200502000-00024. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005. PMID: 15699699
-
Diagnostic assessment of gastroesophageal reflux disease: what is possible vs. what is practical?Hepatogastroenterology. 1992 Feb;39 Suppl 1:3-13. Hepatogastroenterology. 1992. PMID: 1577393 Review.
-
Endoscopic evaluation of gastro-esophageal reflux disease.Yale J Biol Med. 1999 Mar-Jun;72(2-3):93-100. Yale J Biol Med. 1999. PMID: 10780570 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pediatric Gastroenterology Research.Life (Basel). 2023 Aug 25;13(9):1810. doi: 10.3390/life13091810. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37763214 Free PMC article.
-
Is There a Potential Link between Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Recurrent Respiratory Tract Infections in Children?Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jul 7;13(13):2310. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13132310. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37443704 Free PMC article.
-
Gastroesophageal reflux in children: an updated review.Drugs Context. 2019 Jun 17;8:212591. doi: 10.7573/dic.212591. eCollection 2019. Drugs Context. 2019. PMID: 31258618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Iron Deficiency Anemia in Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Dec 26;13(1):63. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13010063. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36611353 Free PMC article.
-
Gastroesophageal Reflux in Children with Asthma.Children (Basel). 2022 Mar 2;9(3):336. doi: 10.3390/children9030336. Children (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35327708 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vandenplas Y, Rudolph CD, Di Lorenzo C, et al. North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition, European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition. Pediatric gastroesophageal reflux clinical practice guidelines: joint recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (NASPGHAN) and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPGHAN). J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2009;49:498–547. - PubMed
-
- Kiljander TO, Junghard O, Beckman O, et al. Effect of esomeprazole 40 mg once or twice daily on asthma: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2010;181:1042–8. - PubMed
-
- Chan WW, Chiou E, Obstein KL, et al. The efficacy of proton pump inhibitors for the treatment of asthma in adults: a meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med 2011;171:620–9. - PubMed
-
- Lightdale JR, Gremse DA. Gastroesophageal reflux: management guidance for the pediatrician. Pediatrics 2013;131:e1684–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

