The Diagnostic Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Differentiating Metastatic Lymph Nodes of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 30213809
- PMCID: PMC7410724
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A5813
The Diagnostic Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Differentiating Metastatic Lymph Nodes of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Accurate lymph node staging is crucial for proper treatment planning for metastasis in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Purpose: Our aim was to evaluate the diagnostic performance of DWI for differentiating metastatic cervical lymph nodes from benign cervical lymph nodes in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and to identify optimal cutoff values for ADC.
Data sources: A computerized literature search was performed to identify relevant original articles in Ovid MEDLINE and EMBASE.
Study selection: Studies evaluating the diagnostic performance of DWI for differentiating metastatic cervical lymph nodes from benign cervical lymph nodes were selected.
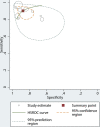
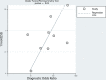
Data analysis: Diagnostic meta-analysis was conducted with a bivariate random-effects model, and a hierarchical summary receiver operating characteristic curve was obtained. Meta-regression was also performed.
Data synthesis: Nine studies with 337 patients were included. In all studies, ADC values derived from metastatic lymph nodes were significantly lower than ADC values derived from benign lymph nodes. The median ADC cutoff value was 0.965 × 10-3 mm2/s. The pooled sensitivity and specificity for the diagnostic performance of DWI in differentiating metastatic lymph nodes from benign lymph nodes were 90% (95% CI, 84%-94%) and 88% (95% CI, 80%-93%), respectively. In the meta-regression, sensitivity was significantly higher in the studies using a 3-mm slice thickness (93% [95% CI, 88%-98%]) than in studies using a slice thickness of >3 mm (86% [95% CI, 77%-95%], P < .01).
Limitations: A small number of studies were included in our meta-analysis.
Conclusions: DWI demonstrated high diagnostic performance for differentiating metastatic lymph nodes from benign lymph nodes in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, and the median ADC cutoff value was 0.965 × 10-3 mm2/s. A 3-mm DWI slice thickness can provide a slight improvement in sensitivity.
© 2018 by American Journal of Neuroradiology.
Figures


References
-
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Head and Neck Cancers V.2.2017. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/head-and-neck.pdf. Accessed January 23, 2018 To view the most recent and complete version of the guidelines, National Comprehensive Cancer Network®, NCCN®, NCCN Guidelines®, and all other NCCN content that are trademarks owned by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc, see www.nccn.org. Accessed January 23, 2018
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
