Prevalence of Hypercholesterolemia, High LDL, and Low HDL in Iran: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 30214097
- PMCID: PMC6123550
Prevalence of Hypercholesterolemia, High LDL, and Low HDL in Iran: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Chronic and abnormal increase of different types of dyslipidemia leads to some important diseases, such as constriction and abstraction of vessels in various parts of the body, especially in the heart. High lipid profile, such as increased total cholesterol and LDL as well as decreased HDL are recognized as cardiovascular disease risk factors. The present study aimed to estimate the prevalence of different types of dyslipidemia in Iran by a meta-analysis method.
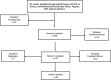
Methods: A literature search for studies published during 1998-2015 was carried out using both Persian and English databases (SID, Magiran, IranMedex, MedLib, PubMed, and Scopus). Keywords such as lipid, dyslipidemia, CVD, cardiovascular risk factors, hypercholesterolemia, high LDL-C, low HDL-C, and prevalence were used in the search. Random-effects model was used for the analysis using STATA (version 11.2).
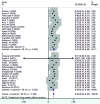
Results: In total, 163 articles were identified of which 49 articles fulfilled the inclusion criteria. The estimated prevalence (95% confidence interval) of eligible articles for high cholesterol ≥200 mg/dl and ≥240 mg/dl was 42% (95% CI: 38-45) and 17% (95% CI: 14-20), respectively. Moreover, the prevalence (95% confidence interval) for high LDL-C ≥130 mg/dl and ≥160 mg/dl was 40% (95% CI: 32-48) and 19% (95% CI: 16-23), respectively. The pooled prevalence estimate for low HDL-C (<40 among males, <50 among females) was 43% (95% CI: 33-53) in both sexes of the Iranian people. All types of lipid component abnormalities (hypercholesterolemia, high LDL-C, and low HDL-C) were more prevalent in women.
Conclusion: The results indicate that the prevalence of different types of dyslipidemia in Iran is substantial. Given the risk of complications (e.g. cardiovascular disease and control of different types of dyslipidemia) in Iranian people, it is important to reduce the burden of cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: Dyslipidemias; Iran; Cardiovascular diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prevalence of dyslipidemia in iran: a systematic review and meta-analysis study.Int J Prev Med. 2014 Apr;5(4):373-93. Int J Prev Med. 2014. PMID: 24829725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidemiology and Prevalence of Dyslipidemia Among Adult Population of Tehran: The Tehran Cohort Study.Arch Iran Med. 2024 Feb 1;27(2):51-61. doi: 10.34172/aim.2024.10. Arch Iran Med. 2024. PMID: 38619028 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of plasma lipid abnormalities and associated risk factors among Iranian adults based on the findings from STEPs survey 2021.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 19;13(1):15499. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42341-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37726324 Free PMC article.
-
High prevalence of low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol concentrations and other dyslipidemic phenotypes in an Iranian population.Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2008 Sep;6(3):187-95. doi: 10.1089/met.2008.0007. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2008. PMID: 18774906
-
Prevalence of dyslipidemia in Iranian children and adolescents: A systematic review.J Res Med Sci. 2015 May;20(5):503-21. doi: 10.4103/1735-1995.163979. J Res Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26487880 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Increased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in patients with type 2 diabetes and its correlates: a cross-sectional, matched case-control survey.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Jul 2;29(1):355. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01950-0. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38956709 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Efficacy Study Combination of Oral Methotrexate and Prednisolone versus Oral Methotrexate in Patients with Lichen Planopilaris.Dermatol Res Pract. 2022 Oct 8;2022:3792489. doi: 10.1155/2022/3792489. eCollection 2022. Dermatol Res Pract. 2022. PMID: 36254319 Free PMC article.
-
Global prevalence of dyslipidemias in the general adult population: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Health Popul Nutr. 2025 Aug 26;44(1):308. doi: 10.1186/s41043-025-01054-3. J Health Popul Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40859400 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the prevalence of cardiometabolic disorders (diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia) diagnosed, undiagnosed, treated, and treatment goal in the elderly: Bushehr Elderly Health Program (BEH).BMC Endocr Disord. 2024 Mar 5;24(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12902-024-01561-0. BMC Endocr Disord. 2024. PMID: 38443972 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of dyslipidaemia among adults in Malaysia.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 7;13(1):11036. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-38275-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37419924 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ghatresamani K, Roghani F, Farokhi A. Evaluation of correaltion between plasma homocysteine and oxidized low-density lipoprotein in patients with coronary artery disease . J Birjand Univ Med Sci. 2009;16:47–53. Persian.
-
- Hassankhani H, Zhinalzadeh A, Fakhri M, Asadi P, Almasi A. Shift work and cardiovascular risk factors in the nurses of the emergency and intensive care wards ofeducational hospitals affiliated to Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences in 2012-2013. Journal of Clinical Research in Paramedical Sciences. 2012;1:55–64. Persian.
-
- Nadimi AE, Ahmadi J. Lipid abnormalities in urban population of Rafsanjan (Rafsanjan coronary risk factors study phase 1) J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2004;3:149–54. Persian.
-
- Jamshidi L, Seif L, Moradi M. Prevalence and association between metabolic syndrome and ischemic heart diseases in patients admitted to the hospitals of Hamedan University of Medical Sciences. Medical Science Journal of Islamic Azad University of Mashhad. 2011;7:101–10. Persian.
-
- Mohamadi-Fard N, Sadri G, Sarraf-Zadegan N, Baghaie A, Shahrokhi S, Hoseini S, et al. The prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors in rural and urban population of Isfahan and Markazi Provinces. J Qazvin Univ Med Sci. 2003;7:5–14. Persian.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
