Characteristics of patients with severe, uncontrolled, eosinophilic asthma enrolled in a French cohort
- PMID: 30214249
- PMCID: PMC6124449
- DOI: 10.2147/JAA.S170866
Characteristics of patients with severe, uncontrolled, eosinophilic asthma enrolled in a French cohort
Abstract
Background and objective: Benralizumab (Fasenra™) has recently been approved as add-on maintenance treatment for adult patients with severe eosinophilic asthma inadequately controlled despite high-dosage inhaled corticosteroids plus long-acting β2-agonists. We aimed to identify and describe the clinical characteristics and disease burden of patients with severe, uncontrolled, eosinophilic asthma in France who may be eligible for treatment with benralizumab.
Patients and methods: This was a retrospective analysis of a prospective, noninterventional, observational study of patients in France enrolled in the Asthma and Bronchial Obstruction Cohort (COBRA). First, we selected adult patients with severe asthma, a documented blood eosinophil count, 12 months of baseline data, and 12 months of follow-up data. Of these study-eligible patients, we next determined the prevalence and described the clinical characteristics and disease burden of patients who would be eligible to receive benralizumab, namely those with ≥2 asthma exacerbations in the previous 12 months and a blood eosinophil count ≥300/μL who were receiving high-dosage inhaled corticosteroids/long-acting β2-agonists.
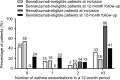
Results: Of the 441 patients eligible for this study, 85 (19%) met the criteria for benralizumab therapy. At study inclusion, benralizumab-eligible patients had a smaller prebronchodilator forced expiratory volume in 1 second and less effective asthma control compared with benralizumab-ineligible patients. During the 12-month follow-up period, benralizumab-eligible patients had greater frequencies of asthma exacerbations and hospitalizations compared with benralizumab-ineligible patients.
Conclusion: Of patients with severe asthma, approximately 20% were qualified for benralizumab treatment. Benralizumab-eligible patients had increased bronchial obstruction, worse asthma control, and a greater frequency of asthma exacerbations and hospitalizations during follow-up care compared with benralizumab-ineligible patients, demonstrating inadequate disease control for these patients.
Keywords: COBRA; France; benralizumab; biologic; eosinophilia.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure Michel Aubier received research grants from AstraZeneca to conduct the study. Gabriel Thabut and Caroline Fabry-Vendrand are employees of AstraZeneca. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Delmas MC, Fuhrman C, for the Epidemiology and Research Group SPLF Clinic Asthma in France: a review of descriptive epidemiological data. Rev Mal Respir. 2010;27(2):151–159. French. - PubMed
-
- Chung KF, Wenzel SE, Brozek JL, et al. International ERS/ATS guidelines on definition, evaluation and treatment of severe asthma. Eur Respir J. 2014;43(2):343–373. - PubMed
-
- Peters SP, Ferguson G, Deniz Y, Reisner C. Uncontrolled asthma: a review of the prevalence, disease burden and options for treatment. Respir Med. 2006;100(7):1139–1151. - PubMed
-
- Gadenne S, Pribil C, Chouaid C, Vergnenegre A, Detournay B. Le coût de l’asthme en France et les implications économiques du niveau de contrôle [The costs of asthma in France and the economic implications of its level of control] Rev Mal Respir. 2011;28(4):419–426. French. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

