Magnoflorine Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury via Suppressing NF-κB and MAPK Activation
- PMID: 30214410
- PMCID: PMC6125611
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00982
Magnoflorine Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury via Suppressing NF-κB and MAPK Activation
Abstract
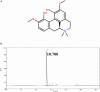
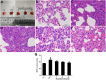
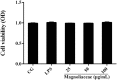
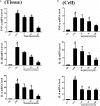
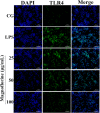
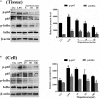
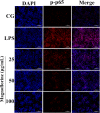
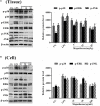
Acute lung injury (ALI) which is featured by a strong pulmonary inflammation, is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in critically ill patients. Magnoflorine, a quaternary alkaloid isolated from Chinese herb Magnolia or Aristolochia, has been reported to have potent anti-inflammatory properties. However, the effect of magnoflorine on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced ALI in mice has not been reported. The purpose of the present study is to investigate the anti-inflammatory effect of magnoflorine on LPS-induced ALI and elucidate its possible molecular mechanisms in RAW264.7 cells. The results of histopathological changes as well as the myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity indicated that magnoflorine significantly alleviated the lung injury induced by LPS. In addition, qPCR results showed that magnoflorine dose-dependently decreased the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. Immunofluorescence assay also confirmed that the level of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) induced by LPS was inhibited by magnoflorine treatment. Further experiments were performed using Western blotting to detect the expression of related proteins in the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. The results showed that magnoflorine suppressed the levels of phosphorylated p65, IκBα, p38, ERK, and JNK. In conclusion, all data indicate that magnoflorine could protect against LPS-induced inflammation in ALI at least partially by inhibiting TLR4-mediated NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways.
Keywords: ALI; LPS; MAPK; NF-κB; anti-inflammation; magnoflorine.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Glycitin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting NF-κB and MAPKs pathway activation in mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Oct;75:105749. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105749. Epub 2019 Jul 12. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31306981
-
Plantamajoside ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via suppressing NF-κB and MAPK activation.Int Immunopharmacol. 2016 Jun;35:315-322. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.04.013. Epub 2016 Apr 16. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27089391
-
Biochanin A protect against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice by regulating TLR4/NF-κB and PPAR-γ pathway.Microb Pathog. 2020 Jan;138:103846. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103846. Epub 2019 Nov 4. Microb Pathog. 2020. PMID: 31698051
-
Kegan Liyan oral liquid ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through inhibition of TLR4-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway and MMP-9 expression.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Jun 20;186:91-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.03.057. Epub 2016 Mar 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27036629
-
Magnoflorine: A review of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and toxicity.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Feb;152:104632. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104632. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 31911246 Review.
Cited by
-
Procyanidin A1 Alleviates Inflammatory Response induced by LPS through NF-κB, MAPK, and Nrf2/HO-1 Pathways in RAW264.7 cells.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 21;9(1):15087. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51614-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31636354 Free PMC article.
-
Necrostatin‑1 protects mice from acute lung injury by suppressing necroptosis and reactive oxygen species.Mol Med Rep. 2020 May;21(5):2171-2181. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11010. Epub 2020 Mar 3. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32323764 Free PMC article.
-
Magnoflorine ameliorates hepatic fibrosis and hepatic stellate cell activation by regulating ferroptosis signaling pathway.Heliyon. 2024 Nov 8;10(22):e39892. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39892. eCollection 2024 Nov 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39634391 Free PMC article.
-
Giloy Ghanvati (Tinospora cordifolia (Willd.) Hook. f. and Thomson) Reversed SARS-CoV-2 Viral Spike-Protein Induced Disease Phenotype in the Xenotransplant Model of Humanized Zebrafish.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 19;12:635510. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.635510. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33953674 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA‑93 contributes to the suppression of lung inflammatory responses in LPS‑induced acute lung injury in mice via the TLR4/MyD88/NF‑κB signaling pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2020 Aug;46(2):561-570. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4610. Epub 2020 May 19. Int J Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32468034 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chiavaroli A., Brunetti L., Orlando G., Recinella L., Ferrante C., Leone S., et al. (2010). Resveratrol inhibits isoprostane production in young and aged rat brain. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 24 441–446. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

