Nerve conduction study of the association between glycemic variability and diabetes neuropathy
- PMID: 30214502
- PMCID: PMC6134701
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-018-0371-0
Nerve conduction study of the association between glycemic variability and diabetes neuropathy
Abstract
Background: It remains unclear whether glycemic variability is related to diabetes microvascular disease, especially diabetes peripheral neuropathy (DPN). We investigated the association between glycemic variability and DPN with type 1 or 2 diabetes.
Methods: Forty patients (23 males and 17 females; aged 34-79 years) underwent continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) and a nerve conduction study (NCS). Glycemic variability was estimated by mean amplitude of glycemic excursions (MAGE) in CGM. DPN was quantitatively evaluated by NCS in the median, tibial, sural and medial plantar nerves.
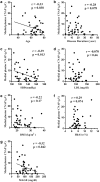
Results: MAGE had a significantly positive correlation with disease duration and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level (r = 0.462, p = 0.003; and r = 0.40, p = 0.011, respectively), and a significantly negative correlation with BMI and medial plantar compound nerve action potential amplitude (r = - 0.39, p = 0.012; and r = - 0.32, p = 0.042, respectively). Multivariate linear regression analysis with adjustment for clinical background showed that MAGE (β = - 0.49, p= 0.007) was independently associated with a higher risk of medial plantar neuropathy.
Conclusions: Glycemic variability may be an independent risk factor for DPN.
Keywords: Continuous glucose monitoring; Diabetes peripheral neuropathy; Glycemic variability; Nerve conduction study.
Figures
References
-
- Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group. Gerstein HC, Miller ME, Byington RP, Goff DC, Jr, Bigger JT, Buse JB, Cushman WC, Genuth S, Ismail-Beigi F, Grimm RH, Jr, Probstfield JL, Simons-Morton DG, Friedewald WT. Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2545–2559. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0802743. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cardoso CRL, Leite NC, Moram CBM, Salles GF. Long-term visit-to-visit glycemic variability as predictor of micro- and macrovascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes: the Rio de Janeiro type 2 diabetes cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018;17:33. doi: 10.1186/s12933-018-0677-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources