Chlorogenic acid in the oxidative stress injury triggered by Shuang-Huang-Lian injection
- PMID: 30214512
- PMCID: PMC6125947
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6567
Chlorogenic acid in the oxidative stress injury triggered by Shuang-Huang-Lian injection
Abstract
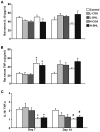
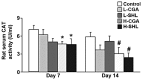
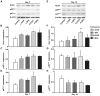
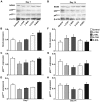
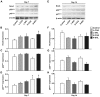
Injections of Chinese herbs are a novel approach to prepare traditional Chinese medicines. However, as injections of Chinese herbs have been extensively used, adverse drug reactions (ADRs) have been on the increase. Additionally, the mechanism for injections of Chinese herbs remains unclear. This study explored the potential role played by chlorogenic acid (CGA) in initiating oxidative stress injury triggered by the utilization of injections of Chinese herbs and the underlying mechanism. A total of 90 male Wistar rats were raised for varying periods by using Shuang-Huang-Lian (SHL) injection or CGA in diverse dosages. Western blot analysis examined the expression of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase subunits, spectrophotometry was used to examine the activity taken by catalase, ELISA was used to examine the concentrations of inflammatory factors in serum, and intravital microscopy was employed to examine the microcirculation. The results showed that the excessive peroxide production induced by CGA in high-dose or SHL in the venule walls may well be through nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase along with a decline in the activity of catalase, and led to imbalance of basal levels of pro-(TNF-α) and anti-(IL-10) inflammatory cytokines. On the basis of the aforementioned results, the mechanism hidden behind the adverse effects of CGA induced by irrational use of Chinese herbal injection can be identified from a deeper perspective.
Keywords: Chinese herbal injection; NADPH oxidase; chlorogenic acid; drug safety; reactive oxygen species.
Figures

References
-
- Ai CL, Xie YM, Li MQ, Wang LX, Liao X. Incidence rate of adverse reaction/event by Qingkailing injection: A Meta-analysis of single rate. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2015;40:4770–4778. (In Chinese) - PubMed
-
- Wang WP, Yu M, Wang L, Jiang XR, Li XB, Wang HW, Cao Y, Liu K, Huang LQ. Academic discussion of adverse reaction of clinical trials of new traditional Chinese medicines and relevant influencing factors. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2015;40:346–350. (In Chinese) - PubMed
-
- Tan LJ, Wang M, Zhu Y. Research progress of adverse reactions of traditional Chinese medicine injections. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2014;39:3889–3898. (In Chinese) - PubMed
-
- Wang ZF, Zhao W, Zhang Y, Xie YM. Analysis of influencing factors on adverse reaction of Shengfu injection based on prospective active safety monitoring. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2015;40:4746–4751. (In Chinese) - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
