Thiazolidinedione induces a therapeutic effect on hepatosteatosis by regulating stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1, lipase activity, leptin and resistin
- PMID: 30214514
- PMCID: PMC6125847
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6563
Thiazolidinedione induces a therapeutic effect on hepatosteatosis by regulating stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1, lipase activity, leptin and resistin
Abstract
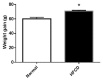
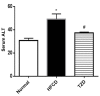
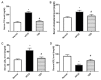
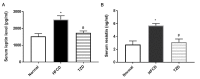
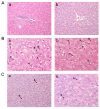
Hepatosteatosis is a disease present worldwide, which presents a number of health problems. Recently, thiazolidinedione (TZD) has been used as a therapy for lipid disorders. The present study demonstrates the potential of TZD as a treatment for hepatosteatosis and its mechanism of action, particularly focusing on its role in lipid metabolism. A total of 60 (80-90 g) rats were divided into three groups: A normal group with a standard diet, a high-fat, high-carbohydrate diet (HFCD) group or a HFCD+TZD group (n=20/group). The HFCD induced hepatosteatosis over a period of 12 weeks and the HFCD+TZD group were administered TZD in weeks 13-16. Blood and tissue samples were collected to measure hepatic function, the lipid profile, metabolism and hormone biomarkers, including serum triglyceride (TG), lipoprotein lipase (LPL), stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD-1), leptin and resistin. The HFCD-fed rats exhibited a significant increase in serum TG, total cholesterol, low-density lipoproteins, alanine transaminase and bilirubin compared with the normal group as well as a significant decrease in high-density lipoprotein. In addition, serum leptin and resistin were significantly elevated in the HFCD group compared with the normal group. The administration of TZD significantly increased SCD-1 activity and significantly inhibited LPL activity. It also attenuated the changes in the lipid profiles and normalized serum leptin and resistin levels. The results of the present study indicated that HFCD induced lipid abnormalities associated with hypertriglyceridemia, hypercholesterolemia and hepatosteatosis. These changes resulted from disruption to leptin and resistin, which may be due to alterations in LPL and SCD-1 activity. TZD mitigated the effects of HFCD-induced hepatosteatosis, indicating a possible regulatory effect of TZD in the development of hepatosteatosis. The authors suggest that the manipulation of SCD-1 and lipase by TZD may be useful as a treatment for hepatosteatosis.
Keywords: hepatosteatosis; high-carbohydrate diet; high-fat; lipase; lipid metabolism; stearoyl-CoA desaturase; thiazolidinedione.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of pioglitazone in antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and insulin sensitivity in a high fat-carbohydrate diet-induced rat model of insulin resistance.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2021 May 24;54(8):e10782. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2020e10782. eCollection 2021. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2021. PMID: 34037093 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of conjugated linoleic acid and troglitazone on lipid accumulation and composition in lean and Zucker diabetic fatty (fa/fa) rats.Lipids. 2006 Mar;41(3):241-7. doi: 10.1007/s11745-006-5093-7. Lipids. 2006. PMID: 16711598
-
Chronic leucine supplementation improves lipid metabolism in C57BL/6J mice fed with a high-fat/cholesterol diet.Food Nutr Res. 2016 Sep 9;60:31304. doi: 10.3402/fnr.v60.31304. eCollection 2016. Food Nutr Res. 2016. PMID: 27616737 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances on stearoyl-Coa desaturase regulation in fatty liver diseases.Curr Drug Metab. 2012 Dec;13(10):1454-63. doi: 10.2174/138920012803762693. Curr Drug Metab. 2012. PMID: 22978399 Review.
-
Regulation of energy metabolism by long-chain fatty acids.Prog Lipid Res. 2014 Jan;53:124-44. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.12.001. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Prog Lipid Res. 2014. PMID: 24362249 Review.
Cited by
-
Dissecting Sex-Related Cognition between Alzheimer's Disease and Diabetes: From Molecular Mechanisms to Potential Therapeutic Strategies.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Mar 5;2021:4572471. doi: 10.1155/2021/4572471. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 33747345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Validation of a Quantification Method for Curcumin Derivatives and Their Hepatoprotective Effects on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022 Jan 15;44(1):409-432. doi: 10.3390/cimb44010029. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35723408 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
