The expression level of CSDAP1 in lung cancer and its clinical significance
- PMID: 30214570
- PMCID: PMC6126166
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.9195
The expression level of CSDAP1 in lung cancer and its clinical significance
Abstract
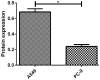
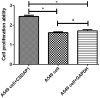
Expression level of messenger RNA (mRNA) of cold shock domain protein A intronless pseudogene (CSDAP1) in lung cancer tissues was studied. Fresh pathological specimens collected from 317 patients with primary lung cancer through surgical resection from January 2007 to January 2012 were selected. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and western blot analysis were used to detect the transcription and translation of CSDAP1 in lung cancer tissues and cancer-adjacent normal tissues, and the results were analyzed in combination with clinicopathological features and prognosis of lung cancer. Among 317 lung cancer specimens, 105 cases (33.1%) had high expression of CSDAP1. Among 138 cases of pulmonary adenocarcinoma, 59 cases had high expression of CSDAP1, and the high expression rate was 42.8%. Among 170 cases of lung squamous cell carcinoma, 46 cases had high expression of CSDAP1, and the high expression rate was 27.5% (P<0.05). Three cases of large cell carcinoma and 9 cases of small cell carcinoma had extremely low expression or had no expression of CSDAP1. Among the 127 lung cancer patients with regional lymph node metastasis, 53 cases (41.7%) had high expression of CSDAP1, while among the 190 lung cancer patients without regional lymph node metastasis, 52 cases (27.4%) had high expression of CSDAP1 (P<0.05). The results also revealed that the expression of CSDAP1 was also related to tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) staging of lung cancer. One-year, three-year and five-year survival rates of lung cancer patients who had no expression of CSDAP1 were relatively high (P<0.05). The results suggested that CSDAP1 may play an important role in the occurrence, development and judgement of prognosis of lung cancer.
Keywords: CSDAP1; RT-PCR; clinical significance; lung cancer; western blot.
Figures
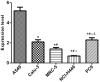

Similar articles
-
Overexpression of Pokemon in non-small cell lung cancer and foreshowing tumor biological behavior as well as clinical results.Lung Cancer. 2008 Oct;62(1):113-9. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2008.02.014. Epub 2008 Jun 11. Lung Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18550205
-
Expression and prognosis of MYOZ2 in gastric cancer.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Sep;22(18):5920-5927. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201809_15921. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30280773
-
[Clinical significance of detecting lymph node micrometastasis of colorectal cancer by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)].Ai Zheng. 2004 Sep;23(9):1069-73. Ai Zheng. 2004. PMID: 15363204 Chinese.
-
[Expression and clinical significance of HMGA2 in renal carcinoma].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2017 Feb 23;39(2):127-132. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2017.02.010. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28219208 Chinese.
-
Overexpression of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) and its clinical significance in lung adenocarcinoma.Lung Cancer. 2009 Nov;66(2):237-44. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2009.02.001. Epub 2009 Mar 3. Lung Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19261348
Cited by
-
Expression of Krüppel-like factor 9 in breast cancer patients and its effect on prognosis.Oncol Lett. 2020 Aug;20(2):1311-1317. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11689. Epub 2020 May 29. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32724373 Free PMC article.
-
Not So Dead Genes-Retrocopies as Regulators of Their Disease-Related Progenitors and Hosts.Cells. 2021 Apr 15;10(4):912. doi: 10.3390/cells10040912. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33921034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pseudogenes as Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets in Human Cancers.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2324:319-337. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1503-4_20. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34165724 Review.
-
Re-recognition of pseudogenes: From molecular to clinical applications.Theranostics. 2020 Jan 1;10(4):1479-1499. doi: 10.7150/thno.40659. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32042317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer, Retrogenes, and Evolution.Life (Basel). 2021 Jan 19;11(1):72. doi: 10.3390/life11010072. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33478113 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xu C, Xie S, Song C, Huang L, Jiang Z. Lin28 mediates cancer chemotherapy resistance via regulation of miRNA signaling. Hepatogastroenterology. 2014;61:1138–1141. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
