Mortality After Complex Displaced Proximal Humerus Fractures in Elderly Patients: Conservative Versus Operative Treatment With Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty
- PMID: 30214828
- PMCID: PMC6134485
- DOI: 10.1177/2151459318795241
Mortality After Complex Displaced Proximal Humerus Fractures in Elderly Patients: Conservative Versus Operative Treatment With Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty
Abstract
Introduction: Proximal humerus fractures (PHFs) are a common fragility fracture and have been shown to increase mortality in elderly patients. In the last decade, reverse total shoulder arthroplasty (RTSA) was introduced as a reliable operative treatment option for this indication. In other fragility fractures, most notably hip fractures, urgent surgical treatment can reduce mortality. The purpose of this study is to evaluate whether treatment with RTSA can reduce 1-year mortality in elderly patients with complex displaced PHFs.
Materials and methods: A retrospective study was performed to compare 1-year mortality between 2 groups of elderly patients (>75 years old) who presented to a level 1 trauma center emergency department with complex displaced PHFs. The conservative treatment group (n = 83; mean age, 83.7 years) presented from 2008 to 2010 when RTSA was not yet available, and treatment was nonoperative. The surgical treatment group (n = 62; mean age, 82.2 years) presented from 2012 to 2015 and underwent RTSA.
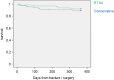
Results: One-year mortality was 8.1% (male 7.1%; female 8.3%) in the surgical treatment group and 10.8% (male 18.8%; female 9.0%) in the conservative treatment group. The reduction in mortality in the surgical treatment group was not significant (entire cohort P = .56; males P = .35; females P = .59).
Discussion: Recent studies failed to show better functional results after surgical treatment with RTSA when compared to conservative treatment. This study suggests that a benefit of surgical treatment with RTSA that was not examined until now might exist-a reduction in the increased mortality risk associated with PHFs.
Conclusions: There was no significant difference in 1-year mortality between the groups, although there was a trend showing lower mortality with RTSA, mostly in men. Further studies with larger populations and longer follow-up times are needed to determine whether this trend is of clinical significance.
Keywords: 1-year mortality; conservative treatment; elderly patients; fragility fractures; proximal humerus fracture; reverse total shoulder arthroplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
5-Year Mortality After Complex Displaced Proximal Humerus Fractures in Elderly Patients: Conservative Versus Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty.J Clin Med. 2024 Dec 31;14(1):167. doi: 10.3390/jcm14010167. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39797250 Free PMC article.
-
Acute versus delayed reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for proximal humeral fractures: a consecutive cohort study.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2022 Feb;31(2):276-285. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2021.07.003. Epub 2021 Aug 13. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2022. PMID: 34400290
-
Trends in the treatment of proximal humerus fractures from 2010 to 2020.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2024 Feb;33(2):e49-e57. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2023.07.038. Epub 2023 Sep 1. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2024. PMID: 37659703
-
The Evolution of Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty and Its Current Use in the Treatment of Proximal Humerus Fractures in the Older Population.J Clin Med. 2022 Sep 30;11(19):5832. doi: 10.3390/jcm11195832. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36233699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Primary Versus Salvage Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty for Displaced Proximal Humerus Fractures in the Elderly: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Shoulder Elb Arthroplast. 2020 Sep 15;4:2471549220949731. doi: 10.1177/2471549220949731. eCollection 2020. J Shoulder Elb Arthroplast. 2020. PMID: 34497963 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Age on Functional Outcome After Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Performed for Proximal Humerus Fractures or Their Sequelae.Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2023;11(1):29-38. doi: 10.22038/ABJS.2022.56366.2798. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2023. PMID: 36793667 Free PMC article.
-
High-Energy Proximal Humerus Fractures in Geriatric Patients: A Review.Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2020 Dec 10;11:2151459320971568. doi: 10.1177/2151459320971568. eCollection 2020. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2020. PMID: 33354380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of predictors of mortality after surgical and non-surgical management in proximal humerus fractures.J Orthop Traumatol. 2021 Nov 3;22(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s10195-021-00606-7. J Orthop Traumatol. 2021. PMID: 34731349 Free PMC article.
-
Cemented vs. cementless stems for reverse shoulder arthroplasty for proximal humerus fractures: a registry analysis with patient-reported outcomes from a level 1 trauma centre.JSES Int. 2024 Oct 3;9(2):415-421. doi: 10.1016/j.jseint.2024.09.023. eCollection 2025 Mar. JSES Int. 2024. PMID: 40182263 Free PMC article.
-
5-Year Mortality After Complex Displaced Proximal Humerus Fractures in Elderly Patients: Conservative Versus Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty.J Clin Med. 2024 Dec 31;14(1):167. doi: 10.3390/jcm14010167. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39797250 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Court-Brown CM, Caesar B. Epidemiology of adult fractures: a review. Injury. 2006;37(8):691–697. - PubMed
-
- Chu SP, Kelsey JL, Keegan TH, et al. Risk factors for proximal humerus fracture. Am J Epidemiol. 2004;160(4):360–367. - PubMed
-
- Court-Brown CM, Garg A, McQueen MM. The epidemiology of proximal humeral fractures. Acta Orthop Scand. 2001;72(4):365–371. - PubMed
-
- Palvanen M, Kannus P, Niemi S, Parkkari J. Update in the epidemiology of proximal humeral fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;442:87–92. - PubMed
-
- Morin S, Lix LM, Azimaee M, Metge C, Caetano P, Leslie WD. Mortality rates after incident non-traumatic fractures in older men and women. Osteoporos Int. 2011;22(9):2439–2448. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources