Effects of shoulder strapping in patients with stroke: A randomised control trial
- PMID: 30214946
- PMCID: PMC6131703
- DOI: 10.4102/sajp.v74i1.430
Effects of shoulder strapping in patients with stroke: A randomised control trial
Abstract
Background: Disability post stroke remains a global problem, with upper limb involvement playing a key role. Shoulder strapping is one of the techniques used clinically to address this.
Objectives: To compare the effect of two shoulder strapping techniques in patients with stroke.
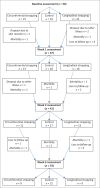
Method: A longitudinal randomised controlled trial included baseline, weeks one, two and six assessments of 56 participants with upper limb hemiplegia. The participants were assessed for shoulder subluxation, shoulder pain, upper limb motor function and muscle tone. They were randomised into control, longitudinal strapping or circumferential strapping groups.
Results: Longitudinal strapping had a non-significant decrease in shoulder subluxation and pain (p > 0.05). Circumferential strapping had no significant effect on any outcomes; however, it prevented the shoulder pain from worsening as much as in the control group (p > 0.05). General improvement in upper limb motor function was observed for all three groups.
Conclusion: Trends in improvement showed that longitudinal strapping could be recommended because it positively influenced shoulder subluxation and pain. Even without significant changes, strapping creates awareness of the limb in patients and caregivers and could be of clinical benefit.
Clinical implication: Longitudinal strapping of the shoulder in patients with stroke seems to positively influence shoulder subluxation and pain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A randomized controlled trial of strapping to prevent post-stroke shoulder pain.Clin Rehabil. 2000 Aug;14(4):370-80. doi: 10.1191/0269215500cr339oa. Clin Rehabil. 2000. PMID: 10945421 Clinical Trial.
-
Strapping the hemiplegic shoulder prevents development of pain during rehabilitation: a randomized controlled trial.Clin Rehabil. 2006 Apr;20(4):287-95. doi: 10.1191/0269215505cr941oa. Clin Rehabil. 2006. PMID: 16719027 Clinical Trial.
-
The California Tri-pull Taping Method in the Treatment of Shoulder Subluxation After Stroke: A Randomized Clinical Trial.N Am J Med Sci. 2016 Apr;8(4):175-82. doi: 10.4103/1947-2714.179933. N Am J Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27213141 Free PMC article.
-
Management of the hemiplegic shoulder complex.Top Stroke Rehabil. 2014 Jul-Aug;21(4):316-8. doi: 10.1310/tsr2104-316. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2014. PMID: 25150663 Review.
-
Hemiplegic shoulder pain: defining the problem and its management.Disabil Rehabil. 2001 Nov 10;23(16):698-705. doi: 10.1080/09638280110062149. Disabil Rehabil. 2001. PMID: 11732559 Review.
Cited by
-
Current stroke rehabilitation services and physiotherapy research in South Africa.S Afr J Physiother. 2019 Jul 22;75(1):475. doi: 10.4102/sajp.v75i1.475. eCollection 2019. S Afr J Physiother. 2019. PMID: 31392288 Free PMC article.
-
Functioning Problems Associated with Health Conditions with Greatest Disease Burden in South Africa: A Scoping Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Nov 24;19(23):15636. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192315636. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36497710 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Shoulder Taping in Treating Hemiplegic Shoulder Subluxation: A Randomized Controlled Study of 35 Patients.Med Sci Monit. 2024 May 31;30:e944222. doi: 10.12659/MSM.944222. Med Sci Monit. 2024. PMID: 38820090 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Ansari N., Naghdi S., Arab T. & Jalaie S, 2008, ‘The interrater and intrarater reliability of the Modified Ashworth Scale in the assessment of muscle spasticity: Limb and muscle group effect’, Neurorehabilitation 23, 231–237. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources