Deafferentation-induced alterations in mitral cell dendritic morphology in the adult zebrafish olfactory bulb
- PMID: 30215151
- PMCID: PMC6450569
- DOI: 10.1007/s10863-018-9772-x
Deafferentation-induced alterations in mitral cell dendritic morphology in the adult zebrafish olfactory bulb
Abstract
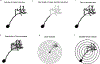
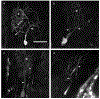
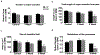
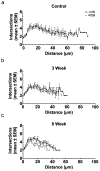
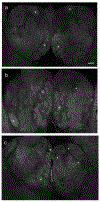
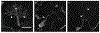
The removal of afferent input to the olfactory bulb by both cautery and chemical olfactory organ ablation in adult zebrafish results in a significant decrease in volume of the ipsilateral olfactory bulb. To examine the effects of deafferentation at a cellular level, primary output neurons of the olfactory bulb, the mitral cells, were investigated using retrograde tract tracing with fluorescent dextran using ex vivo brain cultures. Morphological characteristics including the number of major dendritic branches, total length of dendritic branches, area of the dendritic arbor, overall dendritic complexity, and optical density of the arbor were used to determine the effects of deafferentation on mitral cell dendrites. Following 8 weeks of permanent deafferentation there were significant reductions in the total length of dendritic branches, the area of the dendritic arbor, and the density of fine processes in the dendritic tuft. With 8 weeks of chronic, partial deafferentation there were significant reductions in all parameters examined, including a modified Sholl analysis that showed significant decreases in overall dendritic complexity. These results show the plasticity of mitral cell dendritic structures in the adult brain and provide information about the response of these output neurons following the loss of sensory input in this key model system.
Keywords: Dextran; Modified Sholl analysis; Output neurons; Retrograde labeling; Teleosts.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

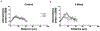
References
-
- Baker H, Kawano T, Albert V, Joh TH, Reis DJ, Margolis FL. 1984. Olfactory bulb dopamine neurons survive deafferentation-induced loss of tyrosine hydroxylase. Neurosci. 11: 605–615 - PubMed
-
- Baker H, Morel K, Stone DM, Maruniak JA. 1993. Adult naris closure profoundly reduces tyrosine hydroxylase expression in mouse olfactory bulb. Brain Res. 614: 109–116 - PubMed
-
- Braubach OR, Fine A, Croll RP. 2012. Distribution and functional organization of glomeruli in the olfactory bulbs of zebrafish (Danio rerio). J Comp Neuro. 520:2317–2339 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

