Adrenocortical function during prolonged critical illness and beyond: a prospective observational study
- PMID: 30215187
- PMCID: PMC6182356
- DOI: 10.1007/s00134-018-5366-7
Adrenocortical function during prolonged critical illness and beyond: a prospective observational study
Abstract
Purpose: For patients suffering from prolonged critical illness, it is unknown whether and when the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis alterations recover, and to what extent adrenocortical function parameters relate to sepsis/septic shock, to clinical need for glucocorticoid treatment, and to survival.
Methods: Patients still in ICU on day 7 (N = 392) and 20 matched healthy subjects were included. Morning blood and 24-h urine were collected daily and cosyntropin tests (250 µg) performed weekly, repeated 1 week after ICU discharge on the regular ward.
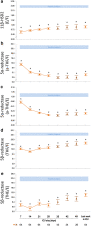
Results: In all patients free of glucocorticoid treatment up until ICU day 28 (N = 347), plasma ACTH always remained low/normal, whereas free cortisol remained high (P ≤ 0.002) explained by reduced binding proteins (P ≤ 0.02) and suppressed cortisol breakdown (P ≤ 0.001). Beyond ICU day 28 (N = 64 long-stayers), plasma (free)cortisol was no longer elevated. One week after ICU discharge, plasma ACTH and (free)cortisol always rose to supra-normal levels (P ≤ 0.006), most pronounced in long-stayers. Long-stayers always showed low incremental total (P ≤ 0.001), but normal incremental free cortisol responses to weekly cosyntropin tests, explained by low cortisol plasma binding proteins. Sepsis/septic shock patients were not different from others, patients subsequently receiving glucocorticoids (N = 45) were not different from those who did not, and non-survivors were distinguishable from survivors only by higher (free)cortisol.
Conclusions: Irrespective of sepsis/septic shock, need for glucocorticoids and survival, low cortisol plasma binding proteins and suppressed cortisol breakdown determine systemic (free)cortisol availability in prolonged critical illness, the latter no longer elevated beyond ICU day 28. The uniform rise in ACTH and cortisol to supra-normal levels 1 week after ICU discharge indicates recovery of a central adrenocortical suppression while in ICU. Low cortisol plasma binding invalidates the cosyntropin test.
Keywords: Adrenal insufficiency; CIRCI; Glucocorticoids; HPA axis; Sepsis; Septic shock.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Comment in
-
Editorial to: Adrenocortical function during prolonged critical illness and beyond: a prospective observational study.Intensive Care Med. 2018 Nov;44(11):1976-1978. doi: 10.1007/s00134-018-5402-7. Epub 2018 Oct 18. Intensive Care Med. 2018. PMID: 30338369 No abstract available.
References
-
- Boonen E, Vervenne H, Meersseman P, Andrew R, Mortier L, Declercq PE, Vanwijngaerden YM, Spriet I, Wouters PJ, Vander PS, Langouche L, Vanhorebeek I, Walker BR, Van den Berghe G. Reduced cortisol metabolism during critical illness. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:1477–1488. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1214969. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vermes I, Beishuizen A, Hampsink RM, Haanen C. Dissociation of plasma adrenocorticotropin and cortisol levels in critically ill patients: possible role of endothelin and atrial natriuretic hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1995;80:1238–1242. - PubMed
-
- Polito A, Sonneville R, Guidoux C, Barrett L, Viltart O, Mattot V, Siami S, de la Grandmaison GL, Chretien F, Singer M, Gray F, Annane D, Brouland JP, Sharshar T. Changes in CRH and ACTH synthesis during experimental and human septic shock. PLoS One. 2011;6:e25905. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025905. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

