Biocompatibility Studies of Gadolinium Complexes with Iminodiacetic Acid Derivatives
- PMID: 30215189
- PMCID: PMC6469645
- DOI: 10.1007/s12011-018-1496-6
Biocompatibility Studies of Gadolinium Complexes with Iminodiacetic Acid Derivatives
Abstract
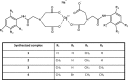
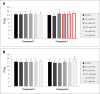
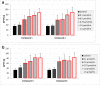
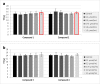
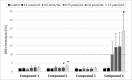
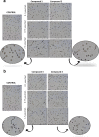
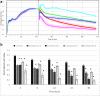
Apart from using as radiopharmaceuticals, iminodiacetic acid derivatives, after complexation with gadolinium, have been also tested as MRI CAs (magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents) since they show high affinity to hepatocytes and therefore provide high-resolution MRI of the liver. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the biocompatibility of four gadolinium complexes with iminodiacetic acid (IDA) derivatives differing in substituent in aromatic ring by estimating their influence on plasma hemostasis, integrity of erythrocyte membrane, and toxicity towards human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). The influence of gadolinium-based CAs on plasma hemostasis was evaluated by measuring PT (prothrombin time), APTT (activated partial tromboplastin time), and TT (thrombin time). The effects of tested compounds on RBCs (Red Blood Cells) were assessed using hemolysis assay and microscopy studies. The influence of gadolinium complexes on the barrier properties of HUVECs was assessed by means of real-time method based on the measurements of the impedance changes of the cells. Gadolinium complexes did not affect significantly PT and TT. APTT measurements revealed significant prolongation in the presence of all tested gadolinium complexes at the concentration higher than 0.5 μmol/mL. Hemolysis assay showed that compounds with alkyl substituents in benzene ring without halogen atom (1-3) do not exert unfavorable effect on the integrity of erythrocyte membrane over the entire concentration range. All gadolinium complexes at 1.0 μmol/mL contribute to the decrease in HUVEC viability and integrity. To conclude, the study describes biocompatibility studies of gadolinium-based CAs, provides additional insight into their potential toxicity associated with systemic administration, and underscores the necessity for further research.
Keywords: Biocompatibility; Gadolinium; Iminodiacetic acid; Magnetic resonance imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synthesis and Biocompatibility Studies of New Iminodiacetic Acid Derivatives.Molecules. 2017 Dec 18;22(12):2265. doi: 10.3390/molecules22122265. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 29258275 Free PMC article.
-
Stability of erythrocyte membrane and overall hemostasis potential - A biocompatibility study of mebrofenin and other iminodiacetic acid derivatives.Pharmacol Rep. 2015 Dec;67(6):1230-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2015.05.021. Epub 2015 Jun 4. Pharmacol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26481547
-
Biocompatible sulfenamide and sulfonamide derivatives of metformin can exert beneficial effects on plasma haemostasis.Chem Biol Interact. 2018 Jan 25;280:15-27. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2017.12.005. Epub 2017 Dec 5. Chem Biol Interact. 2018. PMID: 29217384
-
Extracellular gadolinium-based contrast media: an overview.Eur J Radiol. 2008 May;66(2):160-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2008.01.023. Epub 2008 Mar 20. Eur J Radiol. 2008. PMID: 18358659 Review.
-
Gadolinium(III) complexes as MRI contrast agents: ligand design and properties of the complexes.Dalton Trans. 2008 Jun 21;(23):3027-47. doi: 10.1039/b719704g. Epub 2008 Mar 27. Dalton Trans. 2008. PMID: 18521444 Review.
Cited by
-
Silver Complexes of Miconazole and Metronidazole: Potential Candidates for Melanoma Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 7;25(10):5081. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105081. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791121 Free PMC article.
-
New Iron Metabolic Pathways and Chelation Targeting Strategies Affecting the Treatment of All Types and Stages of Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 13;23(22):13990. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213990. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances on Chelation and Chelator Metal Complexes in Medicine.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 3;21(7):2499. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072499. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32260293 Free PMC article.
-
New Era in the Treatment of Iron Deficiency Anaemia Using Trimaltol Iron and Other Lipophilic Iron Chelator Complexes: Historical Perspectives of Discovery and Future Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 24;22(11):5546. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115546. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34074010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Principles and applications of magnetic nanomaterials in magnetically guided bioimaging.Mater Today Phys. 2023 Mar;32:101003. doi: 10.1016/j.mtphys.2023.101003. Epub 2023 Feb 2. Mater Today Phys. 2023. PMID: 40740662 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balan V, Verestiuc L. Strategies to improve chitosan hemocompatibility: a review. Eur Polym J. 2014;53:171–188. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2014.01.033. - DOI
-
- Dawids S (1993) Test procedures for the blood compatibility of biomaterials. Springer Science+Business Media, BV
-
- Use of International Standard ISO 10993-1. Biological evaluation of medical devices - Part 1: Evaluation and testing within a risk management process
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

