Increased amygdalar metabotropic glutamate receptor 7 mRNA in a genetic mouse model of impaired fear extinction
- PMID: 30215216
- PMCID: PMC6739849
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-018-5031-4
Increased amygdalar metabotropic glutamate receptor 7 mRNA in a genetic mouse model of impaired fear extinction
Abstract
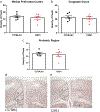
Rationale: Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a devastating anxiety-related disorder which develops subsequent to a severe psychologically traumatic event. Only ~ 9% of people who experience such a trauma develop PTSD. It is clear that a number of factors, including genetics, influence whether an individual will develop PTSD subsequent to a trauma. The 129S1/SvImJ (S1) inbred mouse strain displays poor fear extinction and may be useful to model this specific aspect of PTSD. The metabotropic glutamate receptor 7 (mGlu7 receptor) has previously been shown to be involved in cognitive processes and anxiety-like behaviour placing it in a key position to regulate fear extinction processes. We sought to compare mGlu7 receptor mRNA levels in the S1 strain with those in the robustly extinguishing C57BL/6J (B6) inbred strain using in situ hybridisation (ISH) in three brain regions associated with fear extinction: the amygdala, hippocampus and prefrontal cortex (PFC).
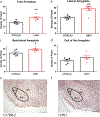
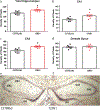
Results: Compared to the B6 strain, S1 mice had increased mGlu7 receptor mRNA levels in the lateral amygdala (LA) and basolateral amygdala (BLA) subdivisions. An increase was also seen in the hippocampal CA1 and CA3 subregions of S1 mice. No difference in mGlu7 receptor levels were seen in the central nucleus (CeA) of the amygdala, dentate gyrus (DG) of the hippocampus or prefrontal cortex.
Conclusions: These data show altered mGlu7 receptor expression in key brain regions associated with fear extinction in two different inbred mouse strains which differ markedly in their fear extinction behaviour. Altered mGlu7 receptor levels may contribute to the deficit fear extinction processes seen in fear extinction in the S1 strain.
Keywords: Post-traumatic stress disorder; Trauma; mGlu7 receptor expression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neural substrates for the distinct effects of presynaptic group III metabotropic glutamate receptors on extinction of contextual fear conditioning in mice.Neuropharmacology. 2013 Mar;66:274-89. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.05.025. Epub 2012 May 27. Neuropharmacology. 2013. PMID: 22643400 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic strain differences in learned fear inhibition associated with variation in neuroendocrine, autonomic, and amygdala dendritic phenotypes.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012 May;37(6):1534-47. doi: 10.1038/npp.2011.340. Epub 2012 Feb 15. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012. PMID: 22334122 Free PMC article.
-
Murine GRPR and stathmin control in opposite directions both cued fear extinction and neural activities of the amygdala and prefrontal cortex.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e30942. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030942. Epub 2012 Feb 1. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22312434 Free PMC article.
-
Stress and Fear Extinction.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016 Jan;41(1):58-79. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.180. Epub 2015 Jun 24. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016. PMID: 26105142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hippocampal network oscillations at the interplay between innate anxiety and learned fear.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Jan;236(1):321-338. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-5109-z. Epub 2018 Nov 11. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30417233 Review.
Cited by
-
Overexpression of mGluR7 in the Prefrontal Cortex Attenuates Autistic Behaviors in Mice.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Jul 15;15:689611. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.689611. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34335187 Free PMC article.
-
The neural circuits and molecular mechanisms underlying fear dysregulation in posttraumatic stress disorder.Front Neurosci. 2023 Dec 5;17:1281401. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1281401. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38116070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Editorial: the psychopharmacology of extinction-from theory to therapy.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Jan;236(1):1-6. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-5152-9. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30604181 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Involvement of the Endocannabinoid, Glutamatergic, and GABAergic Systems in PTSD.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 20;26(13):5929. doi: 10.3390/ijms26135929. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptor function and regulation of sleep-wake cycles.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2023;168:93-175. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2022.11.002. Epub 2023 Jan 13. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36868636 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bradley SR, Uslaner JM, Flick RB, Lee A, Groover KM, Hutson PH (2012) The mGluR7 allosteric agonist AMN082 produces antidepressant-like effects by modulating glutamatergic signaling. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 101:35–40 - PubMed
-
- Breslau N, Kessler RC, Chilcoat HD, Schultz LR, Davis GC, Andreski P (1998) Trauma and posttraumatic stress disorder in the community: the 1996 Detroit area survey of trauma. Arch Gen Psychiatry 55:626–632 - PubMed
-
- Callaerts-Vegh Z, Beckers T, Ball SM, Baeyens F, Callaerts PF, Cryan JF, Molnar E, D’Hooge R (2006) Concomitant deficits in working memory and fear extinction are functionally dissociated from reduced anxiety in metabotropic glutamate receptor 7-deficient mice. J Neurosci 26:6573–6582 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

