Evaluation of the SD Bioline Strep A Ultra Test in Relation With Number of Colony Forming Units and Color Intensity
- PMID: 30215227
- PMCID: PMC6143457
- DOI: 10.3343/alm.2019.39.1.31
Evaluation of the SD Bioline Strep A Ultra Test in Relation With Number of Colony Forming Units and Color Intensity
Abstract
Background: The SD Bioline Strep A Ultra (SD, Yongin, Korea) is a recently developed rapid antigen detection test (RADT) for diagnosing bacterial pharyngitis caused by Group A Streptococcus, We evaluated the performance of SD Bioline Strep A Ultra, using the number of colony forming units and color intensity.
Methods: Three throat swabs each were taken from 343 children with pharyngitis who visited pediatric clinics. We evaluated the performance of SD Bioline Strep A Ultra and compared its positive rate with the number of colony forming units, using the Fisher exact test.
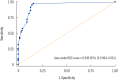
Results: The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value (95% confidence interval) were 97.4% (94.0-99.1%), 90.8% (85.0-94.9%), 93.0% (88.5-96.1%), and 96.5% (92.0-98.9%), respectively. Positive rate significantly differed by number of colony forming units (P=0.021). ROC plot for color intensity showed 0.938 of AUC (area under curve).
Conclusions: SD Bioline Strep A Ultra showed excellent performance, and its positive rate differed by the number of colony counts. This RADT could be used as a sensitive and semi-quantitative method detecting bacterial pharyngitis.
Keywords: Evaluation; Group A Streptococcus; Pharyngitis; Rapid antigen detection test.
© The Korean Society for Laboratory Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The evaluation of SD Bioline Strep A rapid antigen test in acute pharyngitis in pediatric clinics.Korean J Lab Med. 2009 Aug;29(4):320-3. doi: 10.3343/kjlm.2009.29.4.320. Korean J Lab Med. 2009. PMID: 19726894
-
Relationship between the clinical likelihood of group a streptococcal pharyngitis and the sensitivity of a rapid antigen-detection test in a pediatric practice.Pediatrics. 2005 Feb;115(2):280-5. doi: 10.1542/peds.2004-0907. Pediatrics. 2005. PMID: 15687433
-
[Use of the rapid antigen detection test in group A streptococci pharyngitis diagnosis in Tunis, Tunisia].Bull Soc Pathol Exot. 2009 Aug;102(3):175-6. Bull Soc Pathol Exot. 2009. PMID: 19739414 Clinical Trial. French.
-
Evaluating the American Academy of Pediatrics diagnostic standard for Streptococcus pyogenes pharyngitis: backup culture versus repeat rapid antigen testing.Pediatrics. 2003 Jun;111(6 Pt 1):e666-70. doi: 10.1542/peds.111.6.e666. Pediatrics. 2003. PMID: 12777583
-
Spectrum bias of a rapid antigen detection test for group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal pharyngitis in a pediatric population.Pediatrics. 2004 Jul;114(1):182-6. doi: 10.1542/peds.114.1.182. Pediatrics. 2004. PMID: 15231926
References
-
- Choby BA. Diagnosis and treatment of streptococcal pharyngitis. Am Fam Physician. 2009;79:383–390. - PubMed
-
- Edmonson MB, Farwell KR. Relationship between the clinical likelihood of group A streptococcal pharyngitis and the sensitivity of a rapid antigen-detection test in a pediatric practice. Pediatrics. 2005;115:280–285. - PubMed
-
- Kalra MG, Higgins KE, Perez ED. Common questions about streptococcal pharyngitis. Am Fam Phys. 2016;94:24–31. - PubMed
-
- Wessels MR. Clinical practice. Streptococcal pharyngitis. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:648–655. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical