Cardiovascular risk factors in relation to dietary patterns in 50-year-old men and women: a feasibility study of a short FFQ
- PMID: 30215342
- PMCID: PMC10260416
- DOI: 10.1017/S1368980018002264
Cardiovascular risk factors in relation to dietary patterns in 50-year-old men and women: a feasibility study of a short FFQ
Abstract
Objective: We aimed to assess the feasibility of a simple new fifteen-item FFQ as a tool for screening risk of poor dietary patterns in a healthy middle-aged population and to investigate how the results of the FFQ correlated with cardiovascular risk factors and socio-economic factors.
Design: A randomized population-based cross-sectional study. Metabolic measurements for cardiovascular risk factors and information about lifestyle were collected. A fifteen-item FFQ was created to obtain information about dietary patterns. From the FFQ, a healthy eating index was created with three dietary groups: good, average and poor. Multivariate logistic regression was used to assess relationships between dietary patterns and cardiovascular risk factors.
Setting: Sweden.
Subjects: Men and women aged 50 years and living in Gothenburg, Sweden.
Results: In total, 521 middle-aged adults (257 men, 264 women) were examined. With good dietary pattern as the reference, there was a gradient association of having obesity, hypertension and high serum TAG in those with average and poor dietary patterns. After adjustment for education and lifestyle factors, individuals with a poor dietary pattern still had significantly higher risk (OR; 95 % CI) of obesity (2·33; 1·10, 4·94), hypertension (2·73; 1·44, 5·20) and high serum TAG (2·62; 1·33, 5·14) compared with those with a good dietary pattern.
Conclusions: Baseline data collected by a short FFQ can predict cardiovascular risk factors in middle-aged Swedish men and women. The FFQ could be a useful tool in health-care settings, when screening for risk of poor dietary patterns.
Keywords: Cardiovascular risk factors; Dietary patterns; FFQ; Screening.
Figures
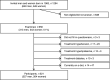
 , poor;
, poor;  , average;
, average;  , good) who were considered to meet the recommendations for each item among 50-year-old men and women born in 1963 and living in Gothenburg, Sweden, 2013. Differences between groups were measured with χ
2 tests: *P<0·05 (pairwise difference between the groups are presented in the online supplementary material, Supplemental Table 1). Good diet meets nine or more recommendations; average diet meets six to eight recommendations; and poor diet meets five or fewer recommendations
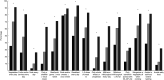
, good) who were considered to meet the recommendations for each item among 50-year-old men and women born in 1963 and living in Gothenburg, Sweden, 2013. Differences between groups were measured with χ
2 tests: *P<0·05 (pairwise difference between the groups are presented in the online supplementary material, Supplemental Table 1). Good diet meets nine or more recommendations; average diet meets six to eight recommendations; and poor diet meets five or fewer recommendations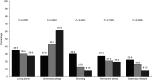
 , poor;
, poor;  , average;
, average;  , good) among 50-year-old men and women born in 1963 and living in Gothenburg, Sweden, 2013. Differences between groups were measured with χ
2 tests (pairwise difference between the groups are presented in the online supplementary material, Supplemental Table 2). Good diet meets nine or more recommendations; average diet meets six to eight recommendations; and poor diet meets five or fewer recommendations
, good) among 50-year-old men and women born in 1963 and living in Gothenburg, Sweden, 2013. Differences between groups were measured with χ
2 tests (pairwise difference between the groups are presented in the online supplementary material, Supplemental Table 2). Good diet meets nine or more recommendations; average diet meets six to eight recommendations; and poor diet meets five or fewer recommendations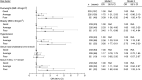
 , model 1 (unadjusted);
, model 1 (unadjusted);  , model 2 (adjusted for education, smoking, sedentary lifestyle and permanent stress). Good diet meets nine or more recommendations; average diet meets six to eight recommendations; and poor diet meets five or fewer recommendations
, model 2 (adjusted for education, smoking, sedentary lifestyle and permanent stress). Good diet meets nine or more recommendations; average diet meets six to eight recommendations; and poor diet meets five or fewer recommendationsReferences
-
- World Health Organization (2014) European Food and Nutrition Action Plan 2015–2020. Copenhagen: WHO Regional Office for Europe.
-
- Nordic Couincil of Ministers (2014) Nordic Nutrition Recommendations 2012: Integrating Nutrition and Physical Activity. Copenhagen: Nordic Council of Ministers.
-
- World Health Organization (2015) World Report on Ageing and Health. Geneva: WHO.
-
- World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research (2007) Food, Nutrition, Physical Activity and the Prevention of Cancer: A Global Perspective. Washington, DC: AICR.
-
- Robertson A, Tirado C, Lobstein T et al. (2004) Food and Health in Europe: A New Basis for Action. WHO Regional Publications, European Series no. 96. Copenhagen: WHO Regional Office for Europe. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

