Long-Term Antipsychotic Effectiveness in First Episode of Psychosis: A 3-Year Follow-Up Randomized Clinical Trial Comparing Aripiprazole, Quetiapine, and Ziprasidone
- PMID: 30215723
- PMCID: PMC6276055
- DOI: 10.1093/ijnp/pyy082
Long-Term Antipsychotic Effectiveness in First Episode of Psychosis: A 3-Year Follow-Up Randomized Clinical Trial Comparing Aripiprazole, Quetiapine, and Ziprasidone
Abstract
Background: Different effectiveness profiles among second-generation antipsychotics may be a key point to optimize treatment in patients suffering a first episode of psychosis to affect long-term outcome. The aim of this study was to compare the clinical effectiveness of aripiprazole, ziprasidone, and quetiapine in the treatment of first episode of psychosis at 3-year follow-up.
Method: From October 2005 to January 2011, a prospective, randomized, open-label study was undertaken. Two hundred-two first-episode, drug-naïve patients were randomly assigned to aripiprazole (n=78), ziprasidone (n =62), or quetiapine (n=62) and followed-up for 3 years. The primary effectiveness measure was all cause of treatment discontinuation. In addition, an analysis based on the intention-to-treat principle was conducted in the analysis for clinical efficacy.
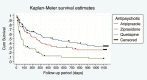
Results: The overall dropout rate at 3 years reached 19.3%. Treatment discontinuation rates were significantly different among treatment groups (aripiprazole=73.08%, ziprasidone=79.03%, and quetiapine=95.16%) (χ2=11.680; P=.001). Statistically significant differences in terms of nonefficacy, nonadherence, and side effects were observed among treatment groups along the 3-year follow-up determining significant differences in time to all-cause discontinuation (log-rank=32.260; P=.001). Significant differences between treatments were found in the categories of sleepiness/sedation (χ2=9.617; P=.008) and increased sleep duration (χ2=6.192; P=.004). No significant differences were found in the profile of extrapyramidal symptoms. Patients on aripiprazole were more likely to be prescribed benzodiazepines.
Conclusions: First-episode psychosis patients on quetiapine were more likely to discontinue treatment due to nonefficacy. Identifying different discontinuation patterns may contribute to optimize treatment selection after first episode of psychosis.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02526030.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antipsychotic Treatment Effectiveness in First Episode of Psychosis: PAFIP 3-Year Follow-Up Randomized Clinical Trials Comparing Haloperidol, Olanzapine, Risperidone, Aripiprazole, Quetiapine, and Ziprasidone.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020 Apr 23;23(4):217-229. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyaa004. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31974576 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment of first-episode non-affective psychosis: a randomized comparison of aripiprazole, quetiapine and ziprasidone over 1 year.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Jan;231(2):357-66. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-3241-3. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 23958945 Clinical Trial.
-
Aripiprazole, Ziprasidone and Quetiapine in the treatment of first-episode nonaffective psychosis: a 12-week randomized, flexible-dose, open-label trial.Schizophr Res. 2013 Jul;147(2-3):375-82. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2013.04.014. Epub 2013 May 1. Schizophr Res. 2013. PMID: 23643328 Clinical Trial.
-
An open, large, 6-month naturalistic study of outcome in schizophrenic outpatients, treated with olanzapine.Hum Psychopharmacol. 2011 Jan;26(1):81-5. doi: 10.1002/hup.1173. Epub 2011 Feb 9. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 23055416 Review.
-
A review of sensitivity and tolerability of antipsychotics in patients with bipolar disorder or schizophrenia: focus on somnolence.J Clin Psychiatry. 2008 Feb;69(2):302-9. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v69n0217. J Clin Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 18211129 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-Term Antipsychotic Effectiveness and Comparison of the Efficacy of Monotherapy and Polypharmacy in Schizophrenia: A 3-Years Follow-Up "Real World" Study in China.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 13;13:860713. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.860713. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35770081 Free PMC article.
-
Antipsychotic Treatment Effectiveness in First Episode of Psychosis: PAFIP 3-Year Follow-Up Randomized Clinical Trials Comparing Haloperidol, Olanzapine, Risperidone, Aripiprazole, Quetiapine, and Ziprasidone.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020 Apr 23;23(4):217-229. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyaa004. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31974576 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Antipsychotic-Induced Constipation: A Review of the Pathogenesis, Clinical Diagnosis, and Treatment.CNS Drugs. 2021 Dec;35(12):1265-1274. doi: 10.1007/s40263-021-00859-0. Epub 2021 Aug 24. CNS Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34427901 Review.
-
Effects of aripiprazole on prolactin levels and differences in effectiveness in patients with schizophrenia: a post-hoc analysis of the real-world data of a multicenter study.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Aug 29;15:1383173. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1383173. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39267697 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Adverse Effects of Psychotropic Drug Therapy: A Systematic Review.Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2023 Aug 12;13(8):1505-1520. doi: 10.3390/ejihpe13080110. Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2023. PMID: 37623307 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Addington D, Addington J, Maticka-Tyndale E(1993)Assessing depression in schizophrenia: the Calgary depression scale. Br J Psychiatry 22:39–44. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Jimenez M, Priede A, Hetrick SE, Bendall S, Killackey E, Parker AG, McGorry PD, Gleeson JF(2012)Risk factors for relapse following treatment for first episode psychosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Schizophr Res 139:116–128 - PubMed
-
- Andreasen N.(1984)The Scale for the Assessment of Positive Symptoms (SAPS). Iowa City: University of Iowa.
-
- Andreasen NC.(1989)Scale for the Assessment of Negative Symptoms (SANS). Br J Psychiatry 155:53–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical