Non-canonical translation initiation of the spliced mRNA encoding the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 basic leucine zipper protein
- PMID: 30215750
- PMCID: PMC6237760
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gky802
Non-canonical translation initiation of the spliced mRNA encoding the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 basic leucine zipper protein
Erratum in
-
Non-canonical translation initiation of the spliced mRNA encoding the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 basic leucine zipper protein.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Feb 20;47(3):1599. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1249. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30566619 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
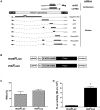
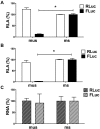
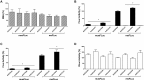
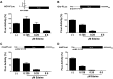
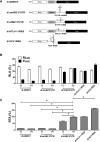
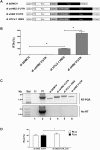
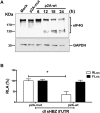
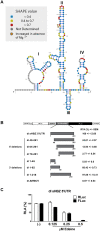
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) is the etiological agent of adult T-cell leukemia (ATL). The HTLV-1 basic leucine zipper protein (HBZ) is expressed in all cases of ATL and is directly associated with virus pathogenicity. The two isoforms of the HBZ protein are synthesized from antisense messenger RNAs (mRNAs) that are either spliced (sHBZ) or unspliced (usHBZ) versions of the HBZ transcript. The sHBZ and usHBZ mRNAs have entirely different 5'untranslated regions (5'UTR) and are differentially expressed in cells, with the sHBZ protein being more abundant. Here, we show that differential expression of the HBZ isoforms is regulated at the translational level. Translation initiation of the usHBZ mRNA relies on a cap-dependent mechanism, while the sHBZ mRNA uses internal initiation. Based on the structural data for the sHBZ 5'UTR generated by SHAPE in combination with 5' and 3' deletion mutants, the minimal region harboring IRES activity was mapped to the 5'end of the sHBZ mRNA. In addition, the sHBZ IRES recruited the 40S ribosomal subunit upstream of the initiation codon, and IRES activity was found to be dependent on the ribosomal protein eS25 and eIF5A.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transcriptional control of spliced and unspliced human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 bZIP factor (HBZ) gene.J Virol. 2008 Oct;82(19):9359-68. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00242-08. Epub 2008 Jul 23. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18653454 Free PMC article.
-
HTLV-I Basic Leucine Zipper Factor (sHBZ) Actively Associates with Nucleophosmin (B23) in the Nucleolus.Viruses. 2025 May 19;17(5):727. doi: 10.3390/v17050727. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40431738 Free PMC article.
-
The 5' untranslated region of the human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 mRNA enables cap-independent translation initiation.J Virol. 2014 Jun;88(11):5936-55. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00279-14. Epub 2014 Mar 12. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24623421 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of HBZ in HTLV-1-Induced Oncogenesis.Viruses. 2016 Feb 2;8(2):34. doi: 10.3390/v8020034. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 26848677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[HTLV-1 bZIP Factor (HBZ): Roles in HTLV-1 Oncogenesis].Bing Du Xue Bao. 2016 Mar;32(2):235-42. Bing Du Xue Bao. 2016. PMID: 27396170 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
The Mytilus chilensis Steamer-like Element-1 Retrotransposon Antisense mRNA Harbors an Internal Ribosome Entry Site That Is Modulated by hnRNPK.Viruses. 2024 Mar 5;16(3):403. doi: 10.3390/v16030403. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38543768 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies of Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 for Persistent Infection: Implications for Leukemogenesis of Adult T-Cell Leukemia-Lymphoma.Front Microbiol. 2020 May 19;11:979. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00979. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32508789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA-Binding Proteins as Regulators of Internal Initiation of Viral mRNA Translation.Viruses. 2022 Jan 19;14(2):188. doi: 10.3390/v14020188. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35215780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polypyrimidine-Tract-Binding Protein Isoforms Differentially Regulate the Hepatitis C Virus Internal Ribosome Entry Site.Viruses. 2022 Dec 20;15(1):8. doi: 10.3390/v15010008. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36680049 Free PMC article.
-
The internal ribosome entry site of the Dengue virus mRNA is active when cap-dependent translation initiation is inhibited.J Virol. 2021 Mar 1;95(5):e01998-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01998-20. Epub 2020 Dec 9. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33298544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murata K., Hayashibara T., Sugahara K., Uemura A., Yamaguchi T., Harasawa H., Hasegawa H., Tsuruda K., Okazaki T., Koji T. et al. . A novel alternative splicing isoform of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 bZIP factor (HBZ-SI) targets distinct subnuclear localization. J. Virol. 2006; 80:2495–2505. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

