Peptide Mimics of the Ribosomal P Stalk Inhibit the Activity of Ricin A Chain by Preventing Ribosome Binding
- PMID: 30217009
- PMCID: PMC6162817
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins10090371
Peptide Mimics of the Ribosomal P Stalk Inhibit the Activity of Ricin A Chain by Preventing Ribosome Binding
Abstract
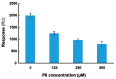
Ricin A chain (RTA) depurinates the sarcin/ricin loop (SRL) by interacting with the C-termini of the ribosomal P stalk. The ribosome interaction site and the active site are located on opposite faces of RTA. The interaction with P proteins allows RTA to depurinate the SRL on the ribosome at physiological pH with an extremely high activity by orienting the active site towards the SRL. Therefore, if an inhibitor disrupts RTA⁻ribosome interaction by binding to the ribosome binding site of RTA, it should inhibit the depurination activity. To test this model, we synthesized peptides mimicking the last 3 to 11 amino acids of P proteins and examined their interaction with wild-type RTA and ribosome binding mutants by Biacore. We measured the inhibitory activity of these peptides on RTA-mediated depurination of yeast and rat liver ribosomes. We found that the peptides interacted with the ribosome binding site of RTA and inhibited depurination activity by disrupting RTA⁻ribosome interactions. The shortest peptide that could interact with RTA and inhibit its activity was four amino acids in length. RTA activity was inhibited by disrupting its interaction with the P stalk without targeting the active site, establishing the ribosome binding site as a new target for inhibitor discovery.
Keywords: P protein interaction; SRL depurination; peptide inhibition; ribosomal P stalk; ricin A chain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The P1/P2 proteins of the human ribosomal stalk are required for ribosome binding and depurination by ricin in human cells.FEBS J. 2012 Oct;279(20):3925-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08752.x. Epub 2012 Sep 11. FEBS J. 2012. PMID: 22909382 Free PMC article.
-
Arginine residues on the opposite side of the active site stimulate the catalysis of ribosome depurination by ricin A chain by interacting with the P-protein stalk.J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 18;288(42):30270-30284. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.510966. Epub 2013 Sep 3. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24003229 Free PMC article.
-
Pentameric organization of the ribosomal stalk accelerates recruitment of ricin a chain to the ribosome for depurination.J Biol Chem. 2010 Dec 31;285(53):41463-71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.171793. Epub 2010 Oct 25. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20974854 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting ricin to the ribosome.Toxicon. 2013 Jul;69:143-51. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2013.02.001. Epub 2013 Feb 20. Toxicon. 2013. PMID: 23454625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of ricin and Shiga toxins with ribosomes.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2012;357:1-18. doi: 10.1007/82_2011_174. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2012. PMID: 21910078 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Leucine 232 and hydrophobic residues at the ribosomal P stalk binding site are critical for biological activity of ricin.Biosci Rep. 2019 Oct 30;39(10):BSR20192022. doi: 10.1042/BSR20192022. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31548364 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-Function Analysis of the A1 Subunit of Shiga Toxin 2 with Peptides That Target the P-Stalk Binding Site and Inhibit Activity.Biochemistry. 2024 Apr 2;63(7):893-905. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.3c00733. Epub 2024 Mar 11. Biochemistry. 2024. PMID: 38467020 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for the interaction of Shiga toxin 2a with a C-terminal peptide of ribosomal P stalk proteins.J Biol Chem. 2020 Nov 13;295(46):15588-15596. doi: 10.1074/jbc.AC120.015070. Epub 2020 Sep 2. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32878986 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Structural Characterization of Ricin Inhibitors Targeting Ribosome Binding Using Fragment-Based Methods and Structure-Based Design.J Med Chem. 2021 Oct 28;64(20):15334-15348. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c01370. Epub 2021 Oct 14. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34648707 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of small molecules at the P-stalk site of ricin A subunit trigger conformational changes that extend into the active site.J Biol Chem. 2025 Mar;301(3):108310. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108310. Epub 2025 Feb 14. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 39955060 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

