Two novel L2HGDH mutations identified in a rare Chinese family with L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria
- PMID: 30217188
- PMCID: PMC6137868
- DOI: 10.1186/s12881-018-0675-9
Two novel L2HGDH mutations identified in a rare Chinese family with L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria
Abstract
Background: L-2-Hydroxyglutaric aciduria (L-2-HGA) is a rare organic aciduria neurometabolic disease that is inherited as an autosomal recessive mode and have a variety of symptoms, such as psychomotor developmental retardation, epilepsy, cerebral symptoms as well as increased concentrations of 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG) in the plasma, urine and cerebrospinal fluid. The causative gene of L-2-HGA is L-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase gene (L2HGDH), which consists of 10 exons.
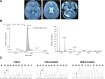
Case presentation: We presented a rare patient primary diagnosis of L-2-HGA based on the clinical symptoms, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) results. Mutational analysis of the L2HGDH gene was performed on the L-2-HGA patient and his parents, which revealed two novel mutations in exon 3: a homozygous missense mutation (c.407 A > G, p.K136R) in both the maternal and paternal allele, and a heterozygous frameshift mutation [c.407 A > G, c.408 del G], (p.K136SfsX3) in the paternal allele. The mutation site p.K136R of the protein was located in the pocket of the FAD/NAD(P)-binding domain and predicted to be pathogenic.
Conclusion: We predicted the homozygous missense mutation (c.407 A > G, p.K136R) was considered as the pathogenic mutation of the patient. The study highlights the power of pedigree analysis in order to interpret novel mutations.
Keywords: L-2-Hydroxyglutaric aciduria; L2HGDH; Mutation.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Written consent was obtained from the patient’s guardians. The study was performed with the approval of the Ethical Committee of the PLA Army General Hospital and was conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for Publication
Consent for publication of the case was obtained for the patient’s guardians, including case description, clinical data and images.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
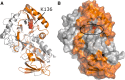
References
-
- Topcu M, Jobard F, Halliez S, Coskun T, Yalcinkayal C, Gerceker FO, Wanders RJ, Prud'homme JF, Lathrop M, Ozguc M, et al. L-2-Hydroxyglutaric aciduria: identification of a mutant gene C14orf160, localized on chromosome 14q22.1. Hum Mol Genet. 2004;13(22):2803–2811. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddh300. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

