Patient-specific in vivo right ventricle material parameter estimation for patients with tetralogy of Fallot using MRI-based models with different zero-load diastole and systole morphologies
- PMID: 30217422
- PMCID: PMC6324966
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.09.030
Patient-specific in vivo right ventricle material parameter estimation for patients with tetralogy of Fallot using MRI-based models with different zero-load diastole and systole morphologies
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Patient-specific in vivo right ventricle material parameter estimation for patients with tetralogy of fallot using MRI-Based models with different zero-load diastole and systole morphologies" [Int. J. Cardiol. 276 (2019) 93-99].Int J Cardiol. 2020 Mar 15;303:87. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2019.09.029. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Int J Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 31623875 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Patient-specific in vivo ventricle material parameter determination is important for cardiovascular investigations. A new cardiac magnetic image (CMR)-based modeling approach with different zero-load diastole and systole geometries was adopted to estimate right ventricle material parameter values for healthy and patients with Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) and seeking potential clinical applications. CMR data were obtained from 6 healthy volunteers and 16 TOF patients with consent obtained. CMR-based RV/LV models were constructed using two zero-load geometries (diastole and systole, 2G model). Material parameter values for begin-filling (BF), end-filling (EF), begin-ejection (BE), and end-ejection (EE) were recorded for analyses. Effective Young's moduli (YM) for fiber direction stress-strain curves were calculated for easy comparisons. The mean EE YM value of TOF patients was 78.6% higher than that of the healthy group (HG). The mean end-ejection YM value from worse-outcome TOF group (WG) post pulmonary valve replacement (PVR) surgery was 59.5% higher than that from the better-outcome TOF group (BG). Using begin-filling YM and end-ejection YM as predictors and the classic logistic regression model to different better-outcome group patients from worse-outcome group patients, the areas under Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves were found to be 0.797 and 0.883 for begin-filling YM and end-ejection YM, respectively. The sensitivity and specificity 0.761 and 0.755 using end-ejection YM as the predictor. This preliminary study suggests that ventricle material stiffness could be a potential parameter to be used to differentiate BG patients from WG patients with further effort and large-scale patient data validations.
Keywords: Myocardium material; Pulmonary valve replacement; Right ventricle mechanical model; Tetralogy of fallot.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None.
Figures
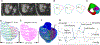
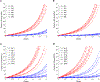
Comment in
-
Computational modelling in congenital heart disease: Challenges and opportunities.Int J Cardiol. 2019 Feb 1;276:116-117. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.11.109. Epub 2018 Nov 22. Int J Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30503188 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Ventricle stress/strain comparisons between Tetralogy of Fallot patients and healthy using models with different zero-load diastole and systole morphologies.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 14;14(8):e0220328. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220328. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31412062 Free PMC article.
-
Patient-Specific MRI-Based Right Ventricle Models Using Different Zero-Load Diastole and Systole Geometries for Better Cardiac Stress and Strain Calculations and Pulmonary Valve Replacement Surgical Outcome Predictions.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 14;11(9):e0162986. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162986. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27627806 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling Active Contraction and Relaxation of Left Ventricle Using Different Zero-load Diastole and Systole Geometries for Better Material Parameter Estimation and Stress/Strain Calculations.Mol Cell Biomech. 2016;13(1):33-55. doi: 10.3970/mcb.2016.013.044. Mol Cell Biomech. 2016. PMID: 29399004 Free PMC article.
-
Regional dysfunction of the right ventricular outflow tract reduces the accuracy of Doppler tissue imaging assessment of global right ventricular systolic function in patients with repaired tetralogy of Fallot.J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2011 Jun;24(6):637-43. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2011.01.020. Epub 2011 Mar 9. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2011. PMID: 21392939
-
Pulmonary valve replacement after operative repair of tetralogy of Fallot: meta-analysis and meta-regression of 3,118 patients from 48 studies.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Dec 10;62(23):2227-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.04.107. Epub 2013 Sep 28. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 24080109
Cited by
-
Right ventricular failure in congenital heart disease.Curr Opin Pediatr. 2019 Oct;31(5):604-610. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0000000000000804. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31356354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Image-Based Finite Element Modeling Approach for Characterizing In Vivo Mechanical Properties of Human Arteries.J Funct Biomater. 2022 Sep 11;13(3):147. doi: 10.3390/jfb13030147. J Funct Biomater. 2022. PMID: 36135582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detailed structural assessment of healthy interventricular septum in the presence of remodeling infarct in the free wall - A finite element model.Heliyon. 2019 Jun 6;5(6):e01841. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01841. eCollection 2019 Jun. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31198871 Free PMC article.
-
Computational Modeling of Right Ventricular Motion and Intracardiac Flow in Repaired Tetralogy of Fallot.Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2022 Feb;13(1):41-54. doi: 10.1007/s13239-021-00558-3. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2022. PMID: 34169460 Free PMC article.
-
Comparisons of simulation results between passive and active fluid structure interaction models for left ventricle in hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy.Biomed Eng Online. 2021 Jan 12;20(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12938-020-00838-4. Biomed Eng Online. 2021. PMID: 33436013 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Christopher AL, Epidemiology of cardiovascular malformations: Prevalence and risk factors, American Journal of Medical Genetics Part C Seminars in Medical Genetics 2000;97:319–325. - PubMed
-
- Julien IEH, Samuel K, The incidence of congenital heart disease, Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2002;39:1890–1900. - PubMed
-
- Lai WW, Luc LM, Cohen MS, Geva T, Echocardiography in pediatric and congenital heart disease: from fetus to adult, John Wiley & Sons, 2015.
-
- Sprengers RW, Roest AAW, Kroft LJM, Tetralogy of Fallot. In:Medical Radiology Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg: 2017.
-
- Apitz C, Gary DW, Andrew NR, Tetralogy of fallot, The Lancet 2009;374:1462–1471. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

