Fibroblast growth factor receptor 5 (FGFR5) is a co-receptor for FGFR1 that is up-regulated in beta-cells by cytokine-induced inflammation
- PMID: 30217817
- PMCID: PMC6222113
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003036
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 5 (FGFR5) is a co-receptor for FGFR1 that is up-regulated in beta-cells by cytokine-induced inflammation
Abstract
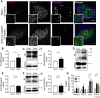
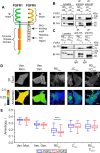
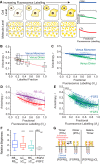
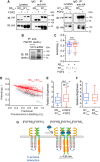
Fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 (FGFR1) activity at the plasma membrane is tightly controlled by the availability of co-receptors and competing receptor isoforms. We have previously shown that FGFR1 activity in pancreatic beta-cells modulates a wide range of processes, including lipid metabolism, insulin processing, and cell survival. More recently, we have revealed that co-expression of FGFR5, a receptor isoform that lacks a tyrosine-kinase domain, influences FGFR1 responses. We therefore hypothesized that FGFR5 is a co-receptor to FGFR1 that modulates responses to ligands by forming a receptor heterocomplex with FGFR1. We first show here increased FGFR5 expression in the pancreatic islets of nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice and also in mouse and human islets treated with proinflammatory cytokines. Using siRNA knockdown, we further report that FGFR5 and FGFR1 expression improves beta-cell survival. Co-immunoprecipitation and quantitative live-cell imaging to measure the molecular interaction between FGFR5 and FGFR1 revealed that FGFR5 forms a mixture of ligand-independent homodimers (∼25%) and homotrimers (∼75%) at the plasma membrane. Interestingly, co-expressed FGFR5 and FGFR1 formed heterocomplexes with a 2:1 ratio and subsequently responded to FGF2 by forming FGFR5/FGFR1 signaling complexes with a 4:2 ratio. Taken together, our findings identify FGFR5 as a co-receptor that is up-regulated by inflammation and promotes FGFR1-induced survival, insights that reveal a potential target for intervention during beta-cell pathogenesis.
Keywords: beta cell (B-cell); cytokine; diabetes; fibroblast growth factor (FGF); fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR); fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET); inflammation; islet; metabolism; pancreas.
© 2018 Regeenes et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
References
-
- Suh J. M., Jonker J. W., Ahmadian M., Goetz R., Lackey D., Osborn O., Huang Z., Liu W., Yoshihara E., and van Dijk T. H., Havinga R., Fan W., Yin Y. Q., Yu R. T., Liddle C., et al. (2014) Endocrinization of FGF1 produces a neomorphic and potent insulin sensitizer. Nature 513, 436–439 10.1038/nature13540 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Silva P. N., Altamentova S. M., Kilkenny D. M., and Rocheleau J. V. (2013) Fibroblast growth factor receptor like-1 (FGFRL1) interacts with SHP-1 phosphatase at insulin secretory granules and induces beta-cell ERK1/2 protein activation. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 17859–17870 10.1074/jbc.M112.440677 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

