Skeletal Muscle Dystrophy mutant of lamin A alters the structure and dynamics of the Ig fold domain
- PMID: 30218058
- PMCID: PMC6138676
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-32227-2
Skeletal Muscle Dystrophy mutant of lamin A alters the structure and dynamics of the Ig fold domain
Abstract
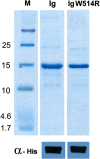
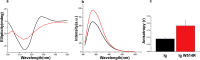
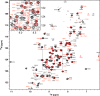
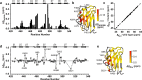
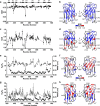
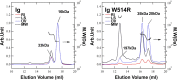
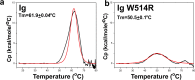
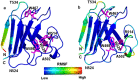
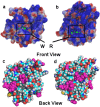
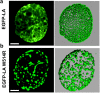
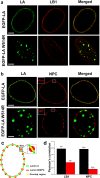
Mutations in the different domains of A-type lamin proteins cause a diverse plethora of diseases collectively termed as laminopathies which can affect multiple organs. Ig fold is one such domain of lamin A which is implicated in numerous nuclear interactions wherein the mutations lead to different laminopathies. W514R is one such mutation in the Ig fold which leads to severe phenotypes in Skeletal Muscle Dystrophy (SMD) which is a class of laminopathies. In this report, we elucidated gross alterations in structure and dynamics at the level of individual amino acids. These studies indicate altered conformational features of residues in the close vicinity of W514. Imaging of mammalian cells transfected with the mutant have shown distinct perturbation of the nuclear meshwork with concomitant alteration in nuclear interactions as a result of increased oligomerization of Ig W514R. Hence, this novel approach of amalgamating theoretical and experimental procedures to predict the severity of a mutant in the context of laminopathies could be extended for numerous lamin A mutants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mapping disease-related missense mutations in the immunoglobulin-like fold domain of lamin A/C reveals novel genotype-phenotype associations for laminopathies.Proteins. 2014 Jun;82(6):904-15. doi: 10.1002/prot.24465. Epub 2013 Dec 26. Proteins. 2014. PMID: 24375749
-
Investigating the differential structural organization and gene expression regulatory networks of lamin A Ig fold domain mutants of muscular dystrophy.Biochem J. 2024 Dec 4;481(23):1803-1827. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20240474. Biochem J. 2024. PMID: 39509247
-
In Silico and In Vivo Analysis of Amino Acid Substitutions That Cause Laminopathies.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 18;22(20):11226. doi: 10.3390/ijms222011226. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681887 Free PMC article.
-
Laminopathies and lamin-associated signaling pathways.J Cell Biochem. 2011 Apr;112(4):979-92. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22992. J Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21400569 Review.
-
Laminopathies; Mutations on single gene and various human genetic diseases.BMB Rep. 2018 Jul;51(7):327-337. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2018.51.7.113. BMB Rep. 2018. PMID: 29764566 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent insight into intermediate filament structure.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2021 Feb;68:132-143. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2020.10.001. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33190098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear pore dysfunction and disease: a complex opportunity.Nucleus. 2024 Dec;15(1):2314297. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2024.2314297. Epub 2024 Feb 21. Nucleus. 2024. PMID: 38383349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PIGB maintains nuclear lamina organization in skeletal muscle of Drosophila.J Cell Biol. 2024 Feb 5;223(2):e202301062. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202301062. Epub 2024 Jan 23. J Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38261271 Free PMC article.
-
The lamin A/C Ig-fold undergoes cell density-dependent changes that alter epitope binding.Nucleus. 2023 Dec;14(1):2180206. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2023.2180206. Nucleus. 2023. PMID: 36809122 Free PMC article.
-
Lamin A/C Mechanotransduction in Laminopathies.Cells. 2020 May 24;9(5):1306. doi: 10.3390/cells9051306. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32456328 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

