EANM practical guidance on uncertainty analysis for molecular radiotherapy absorbed dose calculations
- PMID: 30218316
- PMCID: PMC6208822
- DOI: 10.1007/s00259-018-4136-7
EANM practical guidance on uncertainty analysis for molecular radiotherapy absorbed dose calculations
Abstract
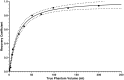
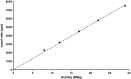
A framework is proposed for modelling the uncertainty in the measurement processes constituting the dosimetry chain that are involved in internal absorbed dose calculations. The starting point is the basic model for absorbed dose in a site of interest as the product of the cumulated activity and a dose factor. In turn, the cumulated activity is given by the area under a time-activity curve derived from a time sequence of activity values. Each activity value is obtained in terms of a count rate, a calibration factor and a recovery coefficient (a correction for partial volume effects). The method to determine the recovery coefficient and the dose factor, both of which are dependent on the size of the volume of interest (VOI), are described. Consideration is given to propagating estimates of the quantities concerned and their associated uncertainties through the dosimetry chain to obtain an estimate of mean absorbed dose in the VOI and its associated uncertainty. This approach is demonstrated in a clinical example.
Keywords: Dosimetry; Uncertainty analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
Jonathan Gear, Katarina Sjögreen Gleisner, and Mark Konijnenberg are members of the EANM Dosimetry Committee, Gerhard Glatting and Glenn Flux are members of the EANM Radiation Protection Committee. All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the principles of the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not describe any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures










References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

