Measuring the wall depletion length of nanoconfined DNA
- PMID: 30219022
- PMCID: PMC6135644
- DOI: 10.1063/1.5040458
Measuring the wall depletion length of nanoconfined DNA
Erratum in
-
Erratum: "Measuring the wall depletion length of nanoconfined DNA" [J. Chem. Phys. 149, 104901 (2018)].J Chem Phys. 2019 Jun 7;150(21):219901. doi: 10.1063/1.5108718. J Chem Phys. 2019. PMID: 31176330 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
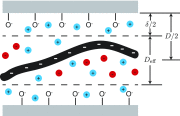
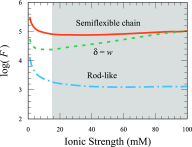
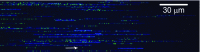
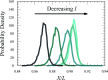
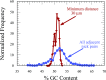
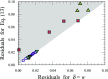
Efforts to study the polymer physics of DNA confined in nanochannels have been stymied by a lack of consensus regarding its wall depletion length. We have measured this quantity in 38 nm wide, square silicon dioxide nanochannels for five different ionic strengths between 15 mM and 75 mM. Experiments used the Bionano Genomics Irys platform for massively parallel data acquisition, attenuating the effect of the sequence-dependent persistence length and finite-length effects by using nick-labeled E. coli genomic DNA with contour length separations of at least 30 µm (88 325 base pairs) between nick pairs. Over 5 × 106 measurements of the fractional extension were obtained from 39 291 labeled DNA molecules. Analyzing the stretching via Odijk's theory for a strongly confined wormlike chain yielded a linear relationship between the depletion length and the Debye length. This simple linear fit to the experimental data exhibits the same qualitative trend as previously defined analytical models for the depletion length but now quantitatively captures the experimental data.
Figures

References
-
- Daoud M. and de Gennes P. G., “Statistics of macromolecular solutions trapped in small pores,” J. Phys. 38, 85–93 (1977). 10.1051/jphys:0197700380108500 - DOI
-
- Odijk T., “The statistics and dynamics of confined or entangled stiff polymers,” Macromolecules 16, 1340–1344 (1983). 10.1021/ma00242a015 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

