Interventions to address social connectedness and loneliness for older adults: a scoping review
- PMID: 30219034
- PMCID: PMC6139173
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-018-0897-x
Interventions to address social connectedness and loneliness for older adults: a scoping review
Abstract
Background: Older adults are at risk for loneliness, and interventions to promote social connectedness are needed to directly address this problem. The nature of interventions aimed to affect the distinct, subjective concepts of loneliness/social connectedness has not been clearly described. The purpose of this review was to map the literature on interventions and strategies to affect loneliness/social connectedness for older adults.
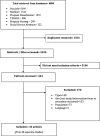
Methods: A comprehensive scoping review was conducted. Six electronic databases were searched from inception in July 2015, resulting in 5530 unique records. Standardized inclusion/exclusion criteria were applied, resulting in a set of 44 studies (reported in 54 articles) for further analysis. Data were extracted to describe the interventions and strategies, and the context of the included studies. Analytic techniques included calculating frequencies, manifest content analysis and meta-summary.
Results: Interventions were described or evaluated in 39 studies, and five studies described strategies to affect loneliness/social connectedness of older adults or their caregivers in a qualitative descriptive study. The studies were often conducted in the United States (38.6%) among community dwelling (54.5%), cognitively intact (31.8%), and female-majority (86.4%) samples. Few focused on non-white participants (4.5%). Strategies described most often were engaging in purposeful activity and maintaining contact with one's social network. Of nine intervention types identified, the most frequently described were One-to-One Personal Contact and Group Activity. Authors held divergent views of why the same type of intervention might impact social connectedness, but social contact was the most frequently conceptualized influencing factor targeted, both within and across intervention types.
Conclusions: Research to test the divergent theories of why interventions work is needed to advance understanding of intervention mechanisms. Innovative conceptualizations of intervention targets are needed, such as purposeful activity, that move beyond the current focus on the objective social network as a way to promote social connectedness for older adults.
Keywords: Intervention; Loneliness; Older adult; Scoping review; Social connectedness.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- O’Rourke HM, Sidani S. Definition, determinants and outcomes of social connectedness for older adults: a scoping review. J Gerontol Nurs. in press - PubMed
-
- Weiss RS. Loneliness: the experience of emotional and social isolation. Cambridge: MIT Press; 1973.
-
- de Jong Gierveld J. A review of loneliness: concept and defintions, determinants and consequences. Rev Clin Gerontol. 1998;8:73–80. doi: 10.1017/S0959259898008090. - DOI
-
- Ericsson I, Hellström I, Kjellström S. Sliding interactions: an ethnography about how persons with dementia interact in housing with care for the elderly. Dementia. 2011;10:523–538. doi: 10.1177/1471301211409376. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical