Up-regulated expression of E2F2 is necessary for p16INK4a-induced cartilage injury
- PMID: 30219053
- PMCID: PMC6138916
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-018-2253-x
Up-regulated expression of E2F2 is necessary for p16INK4a-induced cartilage injury
Abstract
Background: Cartilage degradation would result in osteoarthritis (OA). p16INK4awas found in some age-related diseases. In this study, we aimed to determine the role of p16INK4a during OA and to investigate the underlying mechanisms.
Methods: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was performed to test the activity of senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). Real-time PCR (RT-PCR) and Western blot were used to determine the expressions of target genes.
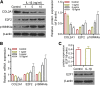
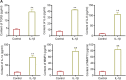
Results: The increased expressions of p16INK4a and E2F2 were accompanied with cartilage degradation induced by IL-1β. Over-expression of p16INK4a enhanced the secretion of SASP markers (TGFβ, IL-6, IL-8, IL-1α, MMP3 and MMP13), reduced the expression of type II procollagen (COL2A1).Thus, the over-expression of p16INK4a lead to cartilage injury. Moreover, we found that the expression of E2F2 was enhanced in p16INK4a over-expression group, and that cartilage injury caused by p16INK4a was alleviated by depleting E2F2.
Conclusions: p16INK4a was up-regulated during the cartilage injury in OA. p16INK4a promoted cartilage injury by increasing the expression of E2F2. Thus, this study extends the molecular regulation network for understanding pathological progression of OA, and provides potential therapeutic target for OA.
Keywords: E2F2; Osteoarthritis (OA); Senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP); p16INK4a.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures




References
-
- Yang Ji Hye, Lee Kiheon, Jung Se Young, Bae Woo Kyung, Ju Hye Jin, Cho In Young, Song Jae Kyeong, Park Hwa Yeon, Han Jong-Soo, Lee Ga-Hye, Bae Ye Seul. Osteoarthritis Affects Health-Related Quality of Life in Korean Adults with Chronic Diseases: The Korea National Health and Nutritional Examination Surveys 2009–2013. Korean Journal of Family Medicine. 2017;38(6):358. doi: 10.4082/kjfm.2017.38.6.358. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dillon CF, Rasch EK, Gu Q, Hirsch R. Prevalence of knee osteoarthritis in the United States: arthritis data from the third National Health and nutrition examination survey 1991-94. J Rheumatol. 2006;33(11):2271–2279. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

