Polymorphonuclear (PMN) elastase in patients after severe traumatic brain injury
- PMID: 30219097
- PMCID: PMC6138888
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-018-0341-x
Polymorphonuclear (PMN) elastase in patients after severe traumatic brain injury
Abstract
Background: Data on PNM elastase levels in cerebrospinal fluid following traumatic brain injury (TBI) in humans are not available in the literature. Therefore, the aim of this prospective study was to evaluate the dynamics of PMN elastase in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of patients after TBI.
Methods: Patients suffering from isolated, closed TBI, presenting with an initial Glasgow coma score ≤ 8 and with intracerebral hemorrhage on the initial cranial computed tomography scan (performed within 90 min after TBI) were enrolled. CSF and blood samples were obtained immediately, 12 h, 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h after admission. ELISA testing was used to quantify the PMN elastase levels in CSF. In addition, the ratio of CSF albumin to serum albumin was calculated to evaluate the role of the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier (BCSFB). As controls, CSF samples were taken from patients receiving spinal anesthesia for elective orthopedic surgery of the lower extremity.
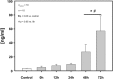
Results: Twenty-three patients meeting the inclusion criteria and ten control patients were enrolled. The PMN elastase showed a significant elevation at 48 and 72 h after TBI. When comparing the PMN elastase levels of patients with intact BCSFB to patients with defective BCSFB, there was no significant difference for the respective observation points.
Conclusions: This is the first study to demonstrate that the PMN elastase levels in CSF significantly increased in the early posttraumatic phase (48 h and 72 h after TBI) in patients. The function of the BCSFB showed no significant influence on the PMN levels.
Keywords: Alpha 1-proteinase; ELISA; PMN; Polymorphonuclear elastase; TBI; Traumatic brain injury.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cerebrospinal s100-B: a potential marker for progressive intracranial hemorrhage in patients with severe traumatic brain injury.Eur J Med Res. 2008 Nov 24;13(11):511-6. Eur J Med Res. 2008. PMID: 19073387
-
Fluid proteomics of CSF and serum reveal important neuroinflammatory proteins in blood-brain barrier disruption and outcome prediction following severe traumatic brain injury: a prospective, observational study.Crit Care. 2021 Mar 12;25(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s13054-021-03503-x. Crit Care. 2021. PMID: 33712077 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of stress doses of hydrocortisone on S-100B vs. interleukin-8 and polymorphonuclear elastase levels in human septic shock.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2005;43(3):259-68. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2005.044. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2005. PMID: 15843228 Clinical Trial.
-
B-Cell Lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) and Regulation of Apoptosis after Traumatic Brain Injury: A Clinical Perspective.Medicina (Kaunas). 2020 Jun 18;56(6):300. doi: 10.3390/medicina56060300. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020. PMID: 32570722 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Characteristics and Outcome in Elderly Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury: For Establishment of Management Strategy.Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2017 Aug 15;57(8):418-425. doi: 10.2176/nmc.st.2017-0058. Epub 2017 Jul 5. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2017. PMID: 28679968 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Brain Trauma and the Secondary Cascade in Humans: Review of the Potential Role of Vitamins in Reparative Processes and Functional Outcome.Behav Sci (Basel). 2023 May 8;13(5):388. doi: 10.3390/bs13050388. Behav Sci (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37232626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial glycocalyx in traumatic brain injury associated coagulopathy: potential mechanisms and impact.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Jun 14;18(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02192-1. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 34126995 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rhind SG, Crnko NT, Baker AJ, Morrison LJ, Shek PN, Scarpelini S, Rizoli SB. Prehospital resuscitation with hypertonic saline-dextran modulates inflammatory, coagulation and endothelial activation marker profiles in severe traumatic brain injured patients. J Neuroinflamm. 2010;7:5. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-7-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials