Type III Interferons in Antiviral Defenses at Barrier Surfaces
- PMID: 30219309
- PMCID: PMC6179363
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2018.08.008
Type III Interferons in Antiviral Defenses at Barrier Surfaces
Abstract
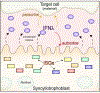
Barrier surfaces such as the epithelium lining the respiratory and gastrointestinal (GI) tracts, the endothelium comprising the blood-brain barrier (BBB), and placental trophoblasts provide key physical and immunological protection against viruses. These barriers utilize nonredundant mechanisms to suppress viral infections including the production of interferons (IFNs), which induce a strong antiviral state following receptor binding. However, whereas type I IFNs control infection systemically, type III IFNs (IFN-λs) control infection locally at barrier surfaces and are often preferentially induced by these cells. In this review we focus on the role of IFN-λ at barrier surfaces, focusing on the respiratory and GI tracts, the BBB, and the placenta, and on how these IFNs act to suppress viral infections.
Keywords: barrier surfaces; innate immunity; interferon; placenta.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

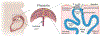
References
-
- Kay H et al. (2011) The Placenta: From Development to Disease, Wiley-Blackwell.
-
- Isaacs A and Lindenmann J (1987) Virus interference. I. The interferon. J. Interferon Res 7, 429–438 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

