Stem cell therapy for neurological disorders: A focus on aging
- PMID: 30219376
- PMCID: PMC6650276
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2018.09.011
Stem cell therapy for neurological disorders: A focus on aging
Abstract
Age-related neurological disorders continue to pose a significant societal and economic burden. Aging is a complex phenomenon that affects many aspects of the human body. Specifically, aging can have detrimental effects on the progression of brain diseases and endogenous stem cells. Stem cell therapies possess promising potential to mitigate the neurological symptoms of such diseases. However, aging presents a major obstacle for maximum efficacy of these treatments. In this review, we discuss current preclinical and clinical literature to highlight the interactions between aging, stem cell therapy, and the progression of major neurological disease states such as Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, stroke, traumatic brain injury, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, multiple sclerosis, and multiple system atrophy. We raise important questions to guide future research and advance novel treatment options.
Keywords: Age-related brain disorders; Cell-therapy; Neurodegenerative diseases; Stroke; Traumatic brain injury.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
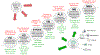
References
-
- Acosta SA, Tajiri N, Shinozuka K, Ishikawa H, Sanberg PR, Sanchez-Ramos J, Song S, Kaneko Y, Borlongan CV, 2014. Combination therapy of human umbilical cord blood cells and granulocyte colony stimulating factor reduces histopathological and motor impairments in an experimental model of chronic traumatic brain injury. PLoS One 9, e90953. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allen SJ, Watson JJ, Shoemark DK, Barua NU, Patel NK, 2013. GDNF, NGF and BDNF as therapeutic options for neurodegeneration. Pharmacol. Ther 138, 155–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

