Outcome in Dilated Cardiomyopathy Related to the Extent, Location, and Pattern of Late Gadolinium Enhancement
- PMID: 30219397
- PMCID: PMC6682609
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2018.07.015
Outcome in Dilated Cardiomyopathy Related to the Extent, Location, and Pattern of Late Gadolinium Enhancement
Abstract
Objectives: This study sought to investigate the association between the extent, location, and pattern of late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) and outcome in a large dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) cohort.
Background: The relationship between LGE and prognosis in DCM is incompletely understood.
Methods: The authors examined the association between LGE and all-cause mortality and a sudden cardiac death (SCD) composite based on the extent, location, and pattern of LGE in DCM.
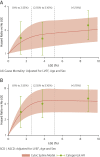
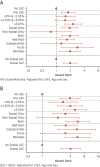
Results: Of 874 patients (588 men, median age 52 years) followed for a median of 4.9 years, 300 (34.3%) had nonischemic LGE. Estimated adjusted hazard ratios for patients with an LGE extent of 0 to 2.55%, 2.55% to 5.10%, and >5.10%, respectively, were 1.59 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.99 to 2.55), 1.56 (95% CI: 0.96 to 2.54), and 2.31 (95% CI: 1.50 to 3.55) for all-cause mortality, and 2.79 (95% CI: 1.42 to 5.49), 3.86 (95% CI: 2.09 to 7.13), and 4.87 (95% CI: 2.78 to 8.53) for the SCD endpoint. There was a marked nonlinear relationship between LGE extent and outcome such that even small amounts of LGE predicted a substantial increase in risk. The presence of septal LGE was associated with increased mortality, but SCD was most associated with the combined presence of septal and free-wall LGE. Predictive models using LGE presence and location were superior to models based on LGE extent or pattern.
Conclusions: In DCM, the presence of septal LGE is associated with a large increase in the risk of death and SCD events, even when the extent is small. SCD risk is greatest with concomitant septal and free-wall LGE. The incremental value of LGE extent beyond small amounts and LGE pattern is limited.
Keywords: cardiovascular magnetic resonance; dilated cardiomyopathy; late gadolinium enhancement.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Are We Ready to Treat Dilated Cardiomyopathy Differently, Using LGE Guidance?JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019 Aug;12(8 Pt 2):1656-1658. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2018.08.005. Epub 2018 Sep 12. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30219396 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gulati A., Jabbour A., Ismail T.F. Association of fibrosis with mortality and sudden cardiac death in patients with nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. JAMA. 2013;309:896–908. - PubMed
-
- Maceira A.M., Prasad S.K., Khan M., Pennell D.J. Normalized left ventricular systolic and diastolic function by steady state free precession cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2006;8:417–426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

