PDZ-RhoGEF Is a Signaling Effector for TROY-Induced Glioblastoma Cell Invasion and Survival
- PMID: 30219706
- PMCID: PMC6140379
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neo.2018.08.008
PDZ-RhoGEF Is a Signaling Effector for TROY-Induced Glioblastoma Cell Invasion and Survival
Abstract
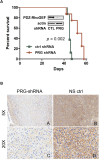
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most common type of malignant brain tumors in adults and has a dismal prognosis. The highly aggressive invasion of malignant cells into the normal brain parenchyma renders complete surgical resection of GBM tumors impossible, increases resistance to therapeutic treatment, and leads to near-universal tumor recurrence. We have previously demonstrated that TROY (TNFRSF19) plays an important role in glioblastoma cell invasion and therapeutic resistance. However, the potential downstream effectors of TROY signaling have not been fully characterized. Here, we identified PDZ-RhoGEF as a binding partner for TROY that potentiated TROY-induced nuclear factor kappa B activation which is necessary for both cell invasion and survival. In addition, PDZ-RhoGEF also interacts with Pyk2, indicating that PDZ-RhoGEF is a component of a signalsome that includes TROY and Pyk2. PDZ-RhoGEF is overexpressed in glioblastoma tumors and stimulates glioma cell invasion via Rho activation. Increased PDZ-RhoGEF expression enhanced TROY-induced glioma cell migration. Conversely, silencing PDZ-RhoGEF expression inhibited TROY-induced glioma cell migration, increased sensitivity to temozolomide treatment, and extended survival of orthotopic xenograft mice. Furthermore, depletion of RhoC or RhoA inhibited TROY- and PDZ-RhoGEF-induced cell migration. Mechanistically, increased TROY expression stimulated Rho activation, and depletion of PDZ-RhoGEF expression reduced this activation. Taken together, these data suggest that PDZ-RhoGEF plays an important role in TROY signaling and provides insights into a potential node of vulnerability to limit GBM cell invasion and decrease therapeutic resistance.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
TROY (TNFRSF19) promotes glioblastoma survival signaling and therapeutic resistance.Mol Cancer Res. 2013 Aug;11(8):865-74. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0008. Epub 2013 May 22. Mol Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23699535 Free PMC article.
-
TROY signals through JAK1-STAT3 to promote glioblastoma cell migration and resistance.Neoplasia. 2020 Sep;22(9):352-364. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2020.06.005. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Neoplasia. 2020. PMID: 32629176 Free PMC article.
-
Propentofylline inhibits glioblastoma cell invasion and survival by targeting the TROY signaling pathway.J Neurooncol. 2016 Feb;126(3):397-404. doi: 10.1007/s11060-015-1981-0. Epub 2015 Nov 12. J Neurooncol. 2016. PMID: 26559543 Free PMC article.
-
Ion channel expression and function in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM): pathophysiological mechanisms and therapeutic potential.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2025 Aug;1872(6):119982. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2025.119982. Epub 2025 May 5. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2025. PMID: 40328081 Review.
-
Tumor Cell Invasion in Glioblastoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 12;21(6):1932. doi: 10.3390/ijms21061932. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32178267 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Leukemia-Associated Rho Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor and Ras Homolog Family Member C Play a Role in Glioblastoma Cell Invasion and Resistance.Am J Pathol. 2020 Oct;190(10):2165-2176. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.07.005. Epub 2020 Jul 18. Am J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32693062 Free PMC article.
-
Optogenetic control of a GEF of RhoA uncovers a signaling switch from retraction to protrusion.Elife. 2025 May 27;12:RP93180. doi: 10.7554/eLife.93180. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40421714 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Rho GTPases in Motility and Invasion of Glioblastoma Cells.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2020 Jan 31;2020:9274016. doi: 10.1155/2020/9274016. eCollection 2020. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2020. PMID: 32089990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the RhoGEF βPIX/COOL-1 in Glioblastoma: Proof of Concept Studies.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Nov 26;12(12):3531. doi: 10.3390/cancers12123531. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33256106 Free PMC article.
-
Using biological constraints to improve prediction in precision oncology.iScience. 2023 Feb 2;26(3):106108. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106108. eCollection 2023 Mar 17. iScience. 2023. PMID: 36852282 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–996. - PubMed
-
- Giese A, Bjerkvig R, Berens ME, Westphal M. Cost of migration: invasion of malignant gliomas and implications for treatment. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:1624–1636. - PubMed
-
- Lefranc F, Brotchi J, Kiss R. Possible future issues in the treatment of glioblastomas: special emphasis on cell migration and the resistance of migrating glioblastoma cells to apoptosis. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:2411–2422. - PubMed
-
- Hu S, Tamada K, Ni J, Vincenz C, Chen L. Characterization of TNFRSF19, a novel member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily. Genomics. 1999;62:103–107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

