Role of ribosome assembly in Escherichia coli ribosomal RNA degradation
- PMID: 30219894
- PMCID: PMC6237783
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gky808
Role of ribosome assembly in Escherichia coli ribosomal RNA degradation
Abstract
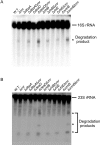
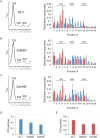
DEAD-Box proteins (DBPs) constitute a prominent class of RNA remodeling factors that play a role in virtually all aspects of RNA metabolism. To better define their cellular functions, deletions in the genes encoding each of the Escherichia coli DBPs were combined with mutations in genes encoding different Ribonucleases (RNases). Significantly, double-deletion strains lacking Ribonuclease R (RNase R) and either the DeaD or SrmB DBP were found to display growth defects and an enhanced accumulation of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) fragments. As RNase R is known to play a key role in removing rRNA degradation products, these observations initially suggested that these two DBPs could be directly involved in the same process. However, additional investigations indicated that DeaD and SrmB-dependent rRNA breakdown is caused by delays in ribosome assembly that increase the exposure of nascent RNAs to endonucleolytic cleavage. Consistent with this notion, mutations in factors known to be important for ribosome assembly also resulted in enhanced rRNA breakdown. Additionally, significant levels of rRNA breakdown products could be visualized in growing cells even in the absence of assembly defects. These findings reveal a hitherto unappreciated mechanism of rRNA degradation under conditions of both normal and abnormal ribosome assembly.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Identification of the sites of action of SrmB, a DEAD-box RNA helicase involved in Escherichia coli ribosome assembly.Mol Microbiol. 2011 Oct;82(2):300-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07779.x. Epub 2011 Aug 22. Mol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21859437
-
Effects of base change mutations within an Escherichia coli ribosomal RNA leader region on rRNA maturation and ribosome formation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 Aug 15;29(16):3394-403. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.16.3394. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001. PMID: 11504877 Free PMC article.
-
Degradation of ribosomal RNA during starvation: comparison to quality control during steady-state growth and a role for RNase PH.RNA. 2011 Feb;17(2):338-45. doi: 10.1261/rna.2448911. Epub 2010 Dec 6. RNA. 2011. PMID: 21135037 Free PMC article.
-
What do we know about ribosomal RNA methylation in Escherichia coli?Biochimie. 2015 Oct;117:110-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2014.11.019. Epub 2014 Dec 13. Biochimie. 2015. PMID: 25511423 Review.
-
Assembly of bacterial ribosomes.Annu Rev Biochem. 2011;80:501-26. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-062608-160432. Annu Rev Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21529161 Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of the leader-trailer helix and antitermination complex in biogenesis of the 30S ribosomal subunit.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jun 9;51(10):5242-5254. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad316. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37102690 Free PMC article.
-
Costs of ribosomal RNA stabilization affect ribosome composition at maximum growth rate.Commun Biol. 2024 Feb 17;7(1):196. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-05815-4. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 38368456 Free PMC article.
-
RNase AM, a 5' to 3' exonuclease, matures the 5' end of all three ribosomal RNAs in E. coli.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jun 4;48(10):5616-5623. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa260. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32343306 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of leader-trailer helices of precursor ribosomal RNA in all phyla of bacteria and archaea.RNA. 2024 Sep 16;30(10):1264-1276. doi: 10.1261/rna.080091.124. RNA. 2024. PMID: 39043438 Free PMC article.
-
Omnipresent Maxwell's demons orchestrate information management in living cells.Microb Biotechnol. 2019 Mar;12(2):210-242. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.13378. Microb Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30806035 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

