Human-accelerated weathering increases salinization, major ions, and alkalinization in fresh water across land use
- PMID: 30220785
- PMCID: PMC6134868
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.02.006
Human-accelerated weathering increases salinization, major ions, and alkalinization in fresh water across land use
Abstract
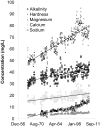
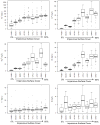
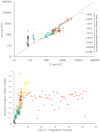
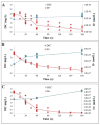
Human-dominated land uses can increase transport of major ions in streams due to the combination of human-accelerated weathering and anthropogenic salts. Calcium, magnesium, sodium, alkalinity, and hardness significantly increased in the drinking water supply for Baltimore, Maryland over almost 50 years (p<0.05) coinciding with regional urbanization. Across a nearby land use gradient at the Baltimore Long-Term Ecological Research (LTER) site, there were significant increases in concentrations of dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC), Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, and Si and pH with increasing impervious surfaces in 9 streams monitored bi-weekly over a 3-4 year period (p<0.05). Base cations in urban streams were up to 60 times greater than forest and agricultural streams, and elemental ratios suggested road salt and carbonate weathering from impervious surfaces as potential sources. Laboratory weathering experiments with concrete also indicated that impervious surfaces increased pH and DIC with potential to alkalinize urban waters. Ratios of Na+ and Cl- suggested that there was enhanced ion exchange in the watersheds from road salts, which could mobilize other base cations from soils to streams. There were significant relationships between Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, and K+ concentrations and Cl-, SO42-, NO3- and DIC across land use (p<0.05), which suggested tight coupling of geochemical cycles. Finally, concentrations of Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, and pH significantly increased with distance downstream (p<0.05) along a stream network draining 170 km2 of the Baltimore LTER site contributing to river alkalinization. Our results suggest that urbanization may dramatically increase major ions, ionic strength, and pH over decades from headwaters to coastal zones, which can impact integrity of aquatic life, infrastructure, drinking water, and coastal ocean alkalinization.
Figures






References
-
- Aquilina L, Poszwa A, Walter C, Vergnaud V, Pierson-Wickmann AC, Ruiz L. Long-Term Effects of High Nitrogen Loads on Cation and Carbon Riverine Export in Agricultural Catchments. Environmental Science & Technology. 2012;46(17):9447–9455. - PubMed
-
- Baker A, Cumberland S, Hudson N. Dissolved and total organic and inorganic carbon in some British rivers. Area. 2008;40(1):117–127.
-
- Barnes RT, Raymond PA. The contribution of agricultural and urban activities to inorganic carbon fluxes within temperate watersheds. Chemical Geology. 2009;266(3–4):318–327.
-
- Berner RA, Lasaga AC, Garrels RM. The carbonate-silicate geochemical cycle and its effect on atmospheric carbon-dioxide over the past 100 million years. American Journal of Science. 1983;283(7):641–683. - PubMed
-
- Bettez ND, Marino R, Howarth RW, Davidson EA. Roads as nitrogen deposition hot spots. Biogeochemistry. 2013;114(1–3):149–163.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
