Modeling Terminologies for Reusability in Faceted Systems
- PMID: 30221256
- PMCID: PMC6136261
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-56157-8_7
Modeling Terminologies for Reusability in Faceted Systems
Abstract
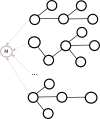
We integrate heterogeneous terminologies into our category-theoretic model of faceted browsing and show that existing terminologies and vocabularies can be reused as facets in a cohesive, interactive system. Commonly found in online search engines and digital libraries, faceted browsing systems depend upon one or more taxonomies which outline the structure and content of the facets available for user interaction. Controlled vocabularies or terminologies are often curated externally and are available as a reusable resource across systems. We demonstrated previously that category theory can abstractly model faceted browsing in a way that supports the development of interfaces capable of reusing and integrating multiple models of faceted browsing. We extend this model by illustrating that terminologies can be reused and integrated as facets across systems with examples from the biomedical domain. Furthermore, we extend our discussion by exploring the requirements and consequences of reusing existing terminologies and demonstrate how categorical operations can create reusable groupings of facets.
Keywords: Category Theory; Faceted Browsing; Information Reuse; Terminologies.
Figures








References
-
- Barr M, Wells C. Category theory for computing science. Prentice Hall; New York: 1990.
-
- Bray T. The javascript object notation (json) data interchange format. 2014 Mar; retrieved June 15, 2016 from https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7159/
-
- Chu HJ, Chow RC. Information Reuse and Integration (IRI), 2010 IEEE International Conference on. IEEE; 2010. An information model for managing domain knowledge via faceted taxonomies; pp. 378–379.
-
- CMS. Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. 2003
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
