Trichoderma gamsii affected herbivore feeding behaviour on Arabidopsis thaliana by modifying the leaf metabolome and phytohormones
- PMID: 30221488
- PMCID: PMC6196387
- DOI: 10.1111/1751-7915.13310
Trichoderma gamsii affected herbivore feeding behaviour on Arabidopsis thaliana by modifying the leaf metabolome and phytohormones
Abstract
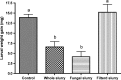
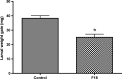
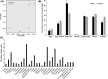
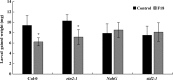
Plants can re-programme their transcriptome, proteome and metabolome to deal with environmental and biotic stress. It has been shown that the rhizosphere microbiome has influence on the plant metabolome and on herbivore behaviour. In the present study, Trichoderma gamsii was isolated from Arabidopsis thaliana rhizosphere soil. The inoculation of roots of Arabidopsis thaliana with T. gamsii significantly inhibited the feeding behaviour of Trichoplusia ni and affected the metabolome as well as the content of phytohormones in Arabidopsis leaves. T. gamsii-treated plant leaves had higher levels of amino acids and lower concentrations of sugars. In addition, T. gamsii-treated plant leaves had more abscisic acid (ABA) and lower levels of salicylic acid (SA) and indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) in comparison with the untreated plants. Furthermore, the inoculation with T. gamsii on different signalling mutants showed that the induction of defences were SA-dependent. These findings indicate that T. gamsii has potential as a new type of biocontrol agent to promote plant repellence to insect attacks.
© 2018 The Authors. Microbial Biotechnology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Society for Applied Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potential impact of soil microbiomes on the leaf metabolome and on herbivore feeding behavior.New Phytol. 2013 Apr;198(1):264-273. doi: 10.1111/nph.12124. Epub 2013 Jan 25. New Phytol. 2013. PMID: 23347044
-
Density-dependent interference of aphids with caterpillar-induced defenses in Arabidopsis: involvement of phytohormones and transcription factors.Plant Cell Physiol. 2015 Jan;56(1):98-106. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcu150. Epub 2014 Oct 22. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25339349
-
Rhizosphere-associated Pseudomonas induce systemic resistance to herbivores at the cost of susceptibility to bacterial pathogens.Mol Ecol. 2018 Apr;27(8):1833-1847. doi: 10.1111/mec.14400. Epub 2017 Nov 23. Mol Ecol. 2018. PMID: 29087012
-
Salicylic acid induced by herbivore feeding antagonizes jasmonic acid mediated plant defenses against insect attack.Plant Signal Behav. 2020;15(1):1704517. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2019.1704517. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Plant Signal Behav. 2020. PMID: 31852340 Free PMC article.
-
The interactions of Trichoderma at multiple trophic levels: inter-kingdom communication.Microbiol Res. 2020 Nov;240:126552. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2020.126552. Epub 2020 Jul 7. Microbiol Res. 2020. PMID: 32659716 Review.
Cited by
-
Trichoderma and its role in biological control of plant fungal and nematode disease.Front Microbiol. 2023 May 3;14:1160551. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1160551. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37206337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural plant disease suppressiveness in soils extends to insect pest control.Microbiome. 2024 Jul 16;12(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s40168-024-01841-w. Microbiome. 2024. PMID: 39014485 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of microRNA-like RNAs from Trichoderma asperellum DQ-1 during its interaction with tomato roots using bioinformatic analysis and high-throughput sequencing.PLoS One. 2021 Jul 22;16(7):e0254808. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0254808. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34293017 Free PMC article.
-
Soil Inoculation Alters Leaf Metabolic Profiles in Genetically Identical Plants.J Chem Ecol. 2020 Aug;46(8):745-755. doi: 10.1007/s10886-020-01156-8. Epub 2020 Feb 5. J Chem Ecol. 2020. PMID: 32020484 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorus-solubilizing Trichoderma spp. from Amazon soils improve soybean plant growth.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 18;10(1):2858. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59793-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32071331 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alfano, G. , Ivey, M.L. , Cakir, C. , Bos, J.I. , Miller, S.A. , Madden, L.V. , et al (2007) Systemic modulation of gene expression in tomato by Trichoderma hamatum 382. Phytopathology 97: 429–437. - PubMed
-
- Badri, D.V. , Zolla, G. , Bakker, M.G. , Manter, D.K. , and Vivanco, J.M. (2013) Potential impact of soil microbiomes on the leaf metabolome and on herbivore feeding behavior. New Phytol 198: 264–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

