High-fructose corn syrup consumption in adolescent rats causes bipolar-like behavioural phenotype with hyperexcitability in hippocampal CA3-CA1 synapses
- PMID: 30221753
- PMCID: PMC6255952
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.14500
High-fructose corn syrup consumption in adolescent rats causes bipolar-like behavioural phenotype with hyperexcitability in hippocampal CA3-CA1 synapses
Abstract
Background and purpose: Children and adolescents are the top consumers of high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS) sweetened beverages. Even though the cardiometabolic consequences of HFCS consumption in adolescents are well known, the neuropsychiatric consequences have yet to be determined.
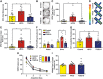
Experimental approach: Adolescent rats were fed for a month with 11% weight/volume carbohydrate containing HFCS solution, which is similar to the sugar-sweetened beverages of human consumption. The metabolic, behavioural and electrophysiological characteristics of HFCS-fed rats were determined. Furthermore, the effects of TDZD-8, a highly specific GSK-3B inhibitor, on the HFCS-induced alterations were further explored.
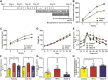
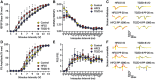
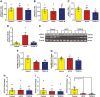
Key results: HFCS-fed adolescent rats displayed bipolar-like behavioural phenotype with hyperexcitability in hippocampal CA3-CA1 synapses. This hyperexcitability was associated with increased presynaptic release probability and increased readily available pool of AMPA receptors to be incorporated into the postsynaptic membrane, due to decreased expression of the neuron-specific α3-subunit of Na+ /K+ -ATPase and an increased ser845 -phosphorylation of GluA1 subunits (AMPA receptor subunit) respectively. TDZD-8 treatment was found to restore behavioural and electrophysiological disturbances associated with HFCS consumption by inhibition of GSK-3B, the most probable mechanism of action of lithium for its mood-stabilizing effects.
Conclusion and implications: This study shows that HFCS consumption in adolescent rats led to a bipolar-like behavioural phenotype with neuronal hyperexcitability, which is known to be one of the earliest endophenotypic manifestations of bipolar disorder. Inhibition of GSK-3B with TDZD-8 attenuated hyperexcitability and restored HFCS-induced behavioural alterations.
© 2018 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High-fructose corn syrup-55 consumption alters hepatic lipid metabolism and promotes triglyceride accumulation.J Nutr Biochem. 2017 Jan;39:32-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2016.09.010. Epub 2016 Sep 30. J Nutr Biochem. 2017. PMID: 27768909
-
Adolescent high-fructose corn syrup consumption leads to dysfunction in adult affective behaviors and mesolimbic proteins in male Sprague-Dawley rats.Behav Brain Res. 2022 Feb 15;419:113687. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113687. Epub 2021 Nov 25. Behav Brain Res. 2022. PMID: 34838930
-
Assessing the effect of sugar type and form of its intake on selected parameters of carbohydrate-lipid metabolism and plasma atherogenic indices in rats.Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig. 2019;70(1):59-67. doi: 10.32394/rpzh.2019.0055. Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig. 2019. PMID: 30837747
-
Fructose and high fructose corn syrup: are they a two-edged sword?Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2021 Aug;72(5):592-614. doi: 10.1080/09637486.2020.1862068. Epub 2021 Jan 26. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 33499690 Review.
-
Does consumption of high-fructose corn syrup beverages cause obesity in children?Pediatr Obes. 2013 Aug;8(4):249-54. doi: 10.1111/j.2047-6310.2013.00173.x. Epub 2013 Apr 29. Pediatr Obes. 2013. PMID: 23630060 Review.
Cited by
-
High Fructose Corn Syrup-Moderate Fat Diet Potentiates Anxio-Depressive Behavior and Alters Ventral Striatal Neuronal Signaling.Front Neurosci. 2021 May 26;15:669410. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.669410. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34121997 Free PMC article.
-
Fructose and Uric Acid as Drivers of a Hyperactive Foraging Response: A Clue to Behavioral Disorders Associated with Impulsivity or Mania?Evol Hum Behav. 2021 May;42(3):194-203. doi: 10.1016/j.evolhumbehav.2020.09.006. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Evol Hum Behav. 2021. PMID: 33994772 Free PMC article.
-
Western Diet Consumption During Development: Setting the Stage for Neurocognitive Dysfunction.Front Neurosci. 2021 Feb 10;15:632312. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.632312. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33642988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early life exposure to high fructose diet induces metabolic dysregulation associated with sex-specific cognitive impairment in adolescent rats.J Nutr Biochem. 2023 Apr;114:109220. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2022.109220. Epub 2022 Nov 23. J Nutr Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36435289 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Boric Acid on Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in Embryonic and Fetal Tissues Damage Caused by Consumption of High-Fructose Corn Syrup in Pregnant Rats.Reprod Sci. 2025 Feb;32(2):514-525. doi: 10.1007/s43032-025-01792-z. Epub 2025 Jan 16. Reprod Sci. 2025. PMID: 39821796 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

