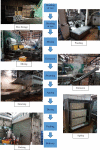
Heat stress in rice vermicelli manufacturing factories
- PMID: 30222068
- PMCID: PMC6237154
- DOI: 10.1080/10773525.2018.1522102
Heat stress in rice vermicelli manufacturing factories
Abstract
Objective: This study provides an assessment of heat stress in indoor rice vermicelli manufacturing factories.
Methods: Worker interviews and heat stress assessments were conducted in food manufacturing factories in Singapore. The Wet Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT) and Heat Stress Index (HSI) were used as heat stress indicators.
Results: The highest WBGT and HSI levels recorded in the rice vermicelli manufacturing factories were 36.68°C and 3777 in the drying and steaming process respectively. These levels were above the recommended permissible HSI and WBGT action limit for heat exposure and considered to be high risk.
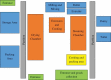
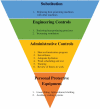
Conclusion: Workers in indoor rice vermicelli manufacturing factories can be exposed to heat stress, and the current measures in place may not be sufficient to protect workers against heat stress injuries. Preventive measures such as engineering controls and heat acclimatization programs are important.
Keywords: Occupational medicine; heat injuries; heat stress; indoor; occupational disease.
Figures
References
-
- Meteorological Service Singapore Past climate trends. Available at: http://www.weather.gov.sg/climate-past-climate-trends/ [Last accessed 2016 May26]
-
- Workplace Safety and Health Council Managing heat stress in the workplace. Workplace Safety and Health Guidelines; 2012.
-
- 2016 TLVs and BEIs Threshold limit values for chemical substances and physical agents and biological exposure indices. Cincinnati, Ohio: American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists; 2016. p. 214.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , National institute for occupational safety and health. Criteria for a recommended standard occupational exposure to heat and hot environments. 2016. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docs/2016-106/pdfs/2016-106.pdf [Last accessed 2016 November11].
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical