Tissue-specific regulation of cytochrome c by post-translational modifications: respiration, the mitochondrial membrane potential, ROS, and apoptosis
- PMID: 30222078
- PMCID: PMC6338631
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.201801417R
Tissue-specific regulation of cytochrome c by post-translational modifications: respiration, the mitochondrial membrane potential, ROS, and apoptosis
Abstract
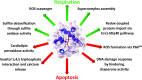
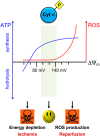
Cytochrome c (Cyt c) plays a vital role in the mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC). In addition, it is a key regulator of apoptosis. Cyt c has multiple other functions including ROS production and scavenging, cardiolipin peroxidation, and mitochondrial protein import. Cyt c is tightly regulated by allosteric mechanisms, tissue-specific isoforms, and post-translational modifications (PTMs). Distinct residues of Cyt c are modified by PTMs, primarily phosphorylations, in a highly tissue-specific manner. These modifications downregulate mitochondrial ETC flux and adjust the mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm), to minimize reactive oxygen species (ROS) production under normal conditions. In pathologic and acute stress conditions, such as ischemia-reperfusion, phosphorylations are lost, leading to maximum ETC flux, ΔΨm hyperpolarization, excessive ROS generation, and the release of Cyt c. It is also the dephosphorylated form of the protein that leads to maximum caspase activation. We discuss the complex regulation of Cyt c and propose that it is a central regulatory step of the mammalian ETC that can be rate limiting in normal conditions. This regulation is important because it maintains optimal intermediate ΔΨm, limiting ROS generation. We examine the role of Cyt c PTMs, including phosphorylation, acetylation, methylation, nitration, nitrosylation, and sulfoxidation and consider their potential biological significance by evaluating their stoichiometry.-Kalpage, H. A., Bazylianska, V., Recanati, M. A., Fite, A., Liu, J., Wan, J., Mantena, N., Malek, M. H., Podgorski, I., Heath, E. I., Vaishnav, A., Edwards, B. F., Grossman, L. I., Sanderson, T. H., Lee, I., Hüttemann, M. Tissue-specific regulation of cytochrome c by post-translational modifications: respiration, the mitochondrial membrane potential, ROS, and apoptosis.
Keywords: electron transport chain; ischemia–reperfusion; phosphorylation; reactive oxygen species; signal transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH), Institute of General Medical Sciences Grant R01 GM116807, and NIH National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke Grants R01 NS091242, and R42 NS105238; the Office of the Assistant Secretary of Defense for Health Affairs through the Peer Reviewed Medical Research Program under Award W81XWH-16-1-0175; and the Karmanos Cancer Institute Prostate Cancer Research Team (PCRT) Postdoctoral Award Program. Opinions, interpretations, conclusions, and recommendations are those of the authors, and are not necessarily endorsed by the funding agencies including the U.S. Department of Defense or the NIH. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Serine-47 phosphorylation of cytochrome c in the mammalian brain regulates cytochrome c oxidase and caspase-3 activity.FASEB J. 2019 Dec;33(12):13503-13514. doi: 10.1096/fj.201901120R. Epub 2019 Sep 28. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 31570002 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylations and Acetylations of Cytochrome c Control Mitochondrial Respiration, Mitochondrial Membrane Potential, Energy, ROS, and Apoptosis.Cells. 2024 Mar 12;13(6):493. doi: 10.3390/cells13060493. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38534337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytochrome c phosphorylation: Control of mitochondrial electron transport chain flux and apoptosis.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2020 Apr;121:105704. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2020.105704. Epub 2020 Feb 2. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32023432 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of Cytochrome c Threonine 28 Regulates Electron Transport Chain Activity in Kidney: IMPLICATIONS FOR AMP KINASE.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jan 6;292(1):64-79. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.744664. Epub 2016 Oct 7. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 27758862 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of mitochondrial respiration and apoptosis through cell signaling: cytochrome c oxidase and cytochrome c in ischemia/reperfusion injury and inflammation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Apr;1817(4):598-609. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2011.07.001. Epub 2011 Jul 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 21771582 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Resistin increases cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells via a mitochondria-mediated pathway.Med Oncol. 2021 Apr 30;38(6):65. doi: 10.1007/s12032-021-01511-z. Med Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33929634
-
Phlorizin ameliorates myocardial fibrosis by inhibiting pyroptosis through restraining HK1-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 31;9(11):e21217. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21217. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38027628 Free PMC article.
-
Lipophilic Cations Rescue the Growth of Yeast under the Conditions of Glycolysis Overflow.Biomolecules. 2020 Sep 20;10(9):1345. doi: 10.3390/biom10091345. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32962296 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria: a breakthrough in combating rheumatoid arthritis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 5;11:1439182. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1439182. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39161412 Free PMC article.
-
Declined expressions of vast mitochondria-related genes represented by CYCS and transcription factor ESRRA in skeletal muscle aging.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):3485-3502. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1948951. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34229541 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li, K., Li, Y., Shelton, J. M., Richardson, J. A., Spencer, E., Chen, Z. J., Wang, X., Williams, R. S. (2000) Cytochrome c deficiency causes embryonic lethality and attenuates stress-induced apoptosis. Cell 101, 389–399 - PubMed
-
- Morriss, G. M., New, D. A. (1979) Effect of oxygen concentration on morphogenesis of cranial neural folds and neural crest in cultured rat embryos. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 54, 17–35 - PubMed
-
- Belikova, N. A., Vladimirov, Y. A., Osipov, A. N., Kapralov, A. A., Tyurin, V. A., Potapovich, M. V., Basova, L. V., Peterson, J., Kurnikov, I. V., Kagan, V. E. (2006) Peroxidase activity and structural transitions of cytochrome c bound to cardiolipin-containing membranes. Biochemistry 45, 4998–5009 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kagan, V. E., Bayir, H. A., Belikova, N. A., Kapralov, O., Tyurina, Y. Y., Tyurin, V. A., Jiang, J., Stoyanovsky, D. A., Wipf, P., Kochanek, P. M., Greenberger, J. S., Pitt, B., Shvedova, A. A., Borisenko, G. (2009) Cytochrome c/cardiolipin relations in mitochondria: a kiss of death. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 46, 1439–1453 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

