A novel pH-dependent membrane peptide that binds to EphA2 and inhibits cell migration
- PMID: 30222105
- PMCID: PMC6192698
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.36645
A novel pH-dependent membrane peptide that binds to EphA2 and inhibits cell migration
Abstract
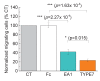
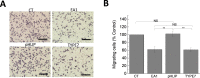
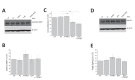
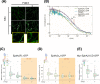
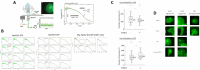
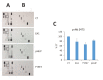
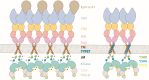
Misregulation of the signaling axis formed by the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) EphA2 and its ligand, ephrinA1, causes aberrant cell-cell contacts that contribute to metastasis. Solid tumors are characterized by an acidic extracellular medium. We intend to take advantage of this tumor feature to design new molecules that specifically target tumors. We created a novel pH-dependent transmembrane peptide, TYPE7, by altering the sequence of the transmembrane domain of EphA2. TYPE7 is highly soluble and interacts with the surface of lipid membranes at neutral pH, while acidity triggers transmembrane insertion. TYPE7 binds to endogenous EphA2 and reduces Akt phosphorylation and cell migration as effectively as ephrinA1. Interestingly, we found large differences in juxtamembrane tyrosine phosphorylation and the extent of EphA2 clustering when comparing TYPE7 with activation by ephrinA1. This work shows that it is possible to design new pH-triggered membrane peptides to activate RTK and gain insights on its activation mechanism.
Keywords: EphA2 activation; membrane active peptide; molecular biophysics; none; pH responsive; receptor tyrosine kinase; structural biology.
© 2018, Alves et al.
Conflict of interest statement
DA, JW, XS, VN, KS, KB, SK, JM, BW, SA, AS, FB No competing interests declared
Figures
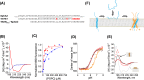
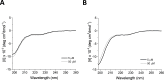
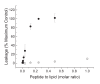
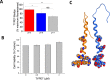






References
-
- Anbazhagan V, Schneider D. The membrane environment modulates self-association of the human GpA TM domain--implications for membrane protein folding and transmembrane signaling. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes. 2010;1798:1899–1907. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2010.06.027. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arpel A, Sawma P, Spenlé C, Fritz J, Meyer L, Garnier N, Velázquez-Quesada I, Hussenet T, Aci-Sèche S, Baumlin N, Genest M, Brasse D, Hubert P, Crémel G, Orend G, Laquerrière P, Bagnard D. Transmembrane domain targeting peptide antagonizing ErbB2/Neu inhibits breast tumor growth and metastasis. Cell Reports. 2014;8:1714–1721. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.07.044. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

