Cognition and renal function: findings from a Brazilian population
- PMID: 30222178
- PMCID: PMC6699443
- DOI: 10.1590/2175-8239-jbn-2018-0067
Cognition and renal function: findings from a Brazilian population
Abstract
Introduction: The prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) is increasing, with a potential impact in the risk of acceleration of dementia. The potential association between glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and cognitive performance was scarcely studied. The aim of this study was to evaluate cognitive performance levels across different degrees of kidney function.
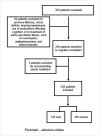
Methods: We analyzed 240 outpatients in a nephrology service, classified according to eGFR: Advanced (≤ 30ml/min/1.73m2), Moderate (30,1ml/min/1.73m2 to ≤ 60ml/min/1.73m2), and Mild CKD (> 60ml/min/1.73m2). Word list memory, Semantic fluency, Mental State Mini Exam and Trail Making Test (TMT) were applied to evaluate cognitive performance. In the TMT, lower scores are associated with better cognition. In linear regression, cognitive function was considered as dependent variables while groups based on eGFR were considered explanatory variables. The group with eGFR > 60ml/min was the reference and models were adjusted for confounding factors.
Results: In our population (n = 240) 64 patients (26.7%) were classified as having advanced, 98(40,8%) moderate, and 78(32,5%) mild. There was no statistical difference among them in MMSE or in the verbal fluency test. However, comparing to mild, patients with advanced CKD presented significantly worse cognitive performance measured by TMTA [50,8s ± 31.1s versus 66,6s ± 35,7s (p = 0.016)] and TMTB [92,7s ± 46,2s versus 162,4s ± 35,7s (p < 0.001)]. Significantly lower TMTB scores (CI95%) 33,0s (4,5-61,6s) were observed in patients with mild compared to advanced CKD in the multivariate analysis adjusting for age, education, sex, diabetes, and alcohol use.
Conclusion: Advanced CKD is independently associated with poorer cognitive performance measured by an executive performance test compared to mild CKD.
References
-
- Global Burden of Disease Study 2013 Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2015;386:743-800. - PMC - PubMed
- Global Burden of Disease Study 2013 Collaborators Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;386:743–800. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barreto SM, Ladeira RM, Duncan BB, Schmidt MI, Lopes AA, Benseñor IM, et al. Chronic kidney disease among adult participants of the ELSA-Brasil cohort: association with race and socioeconomic position. J Epidemiol Community Health 2016;70:380-9. - PubMed
- Barreto SM, Ladeira RM, Duncan BB, Schmidt MI, Lopes AA, Benseñor IM, et al. Chronic kidney disease among adult participants of the ELSA-Brasil cohort: association with race and socioeconomic position. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2016;70:380–389. - PubMed
-
- Schneider SM, Kielstein JT, Braverman J, Novak M. Cognitive Function in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease: Challenges in Neuropsychological Assessments. Semin Nephrol 2015;35:304-10. - PubMed
- Schneider SM, Kielstein JT, Braverman J, Novak M. Cognitive Function in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease: Challenges in Neuropsychological Assessments. Semin Nephrol. 2015;35:304–310. - PubMed
-
- KDIGO. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int Suppl 2012;3:S1-150.
- KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2012;3:S1–150.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous