Albumin and hemoglobin adducts of estrogen quinone as biomarkers for early detection of breast cancer
- PMID: 30222738
- PMCID: PMC6141067
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201241
Albumin and hemoglobin adducts of estrogen quinone as biomarkers for early detection of breast cancer
Abstract
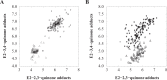
Cumulative estrogen concentration is an important determinant of the risk of developing breast cancer. Estrogen carcinogenesis is attributed to the combination of receptor-driven mitogenesis and DNA damage induced by quinonoid metabolites of estrogen. The present study was focused on developing an improved breast cancer prediction model using estrogen quinone-protein adduct concentrations. Blood samples from 152 breast cancer patients and 71 healthy women were collected, and albumin (Alb) and hemoglobin (Hb) adducts of estrogen-3,4-quinone and estrogen-2,3-quinone were extracted and evaluated as potential biomarkers of breast cancer. A multilayer perceptron (MLP) was used as the predictor model and the resultant prediction of breast cancer was more accurate than other existing detection methods. A MLP using the logarithm of the concentrations of the estrogen quinone-derived adducts (four input nodes, 10 hidden nodes, and one output node) was used to predict breast cancer risk with accuracy close to 100% and area under curve (AUC) close to one. The AUC value of one showed that both data sets were separable. We conclude that Alb and Hb adducts of estrogen quinones are promising biomarkers for the early detection of breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Imbalances in the disposition of estrogen and naphthalene in breast cancer patients: a potential biomarker of breast cancer risk.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 16;10(1):11773. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68814-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32678225 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of estrogen quinone-derived protein adducts and their identification in human serum albumin derived from breast cancer patients and healthy controls.Toxicol Lett. 2011 May 10;202(3):244-52. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2011.02.010. Epub 2011 Feb 24. Toxicol Lett. 2011. PMID: 21354283
-
Hemoglobin adducts as biomarkers of estrogen homeostasis: elevation of estrogenquinones as a risk factor for developing breast cancer in Taiwanese women.Toxicol Lett. 2014 Mar 21;225(3):386-91. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2014.01.004. Epub 2014 Jan 19. Toxicol Lett. 2014. PMID: 24447770
-
Catechol estrogen quinones as initiators of breast and other human cancers: implications for biomarkers of susceptibility and cancer prevention.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Aug;1766(1):63-78. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2006.03.001. Epub 2006 Apr 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16675129 Review.
-
Critical depurinating DNA adducts: Estrogen adducts in the etiology and prevention of cancer and dopamine adducts in the etiology and prevention of Parkinson's disease.Int J Cancer. 2017 Sep 15;141(6):1078-1090. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30728. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Int J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28388839 Review.
Cited by
-
Detection and Characterization of Catechol Quinone-Derived Protein Adducts Using Biomolecular Mass Spectrometry.Front Chem. 2019 Aug 21;7:571. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00571. eCollection 2019. Front Chem. 2019. PMID: 31497592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogenized HSA induced high-affinity autoantibodies in breast cancer - Novel biomarker for early detection.Front Oncol. 2024 Nov 27;14:1493320. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1493320. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39664179 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the Abasic Sites in Breast Cancer Patients With 5 Year Postoperative Treatment Without Recurrence in Taiwan.Cancer Control. 2024 Jan-Dec;31:10732748241300656. doi: 10.1177/10732748241300656. Cancer Control. 2024. PMID: 39520259 Free PMC article.
-
Imbalances in the disposition of estrogen and naphthalene in breast cancer patients: a potential biomarker of breast cancer risk.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 16;10(1):11773. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68814-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32678225 Free PMC article.
-
Mass Spectrometry-Based Methodologies for Targeted and Untargeted Identification of Protein Covalent Adducts (Adductomics): Current Status and Challenges.High Throughput. 2019 Apr 23;8(2):9. doi: 10.3390/ht8020009. High Throughput. 2019. PMID: 31018479 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous